Fig. 6 |. Autonomous retinal-imaging results in freestanding individuals with undilated eyes.
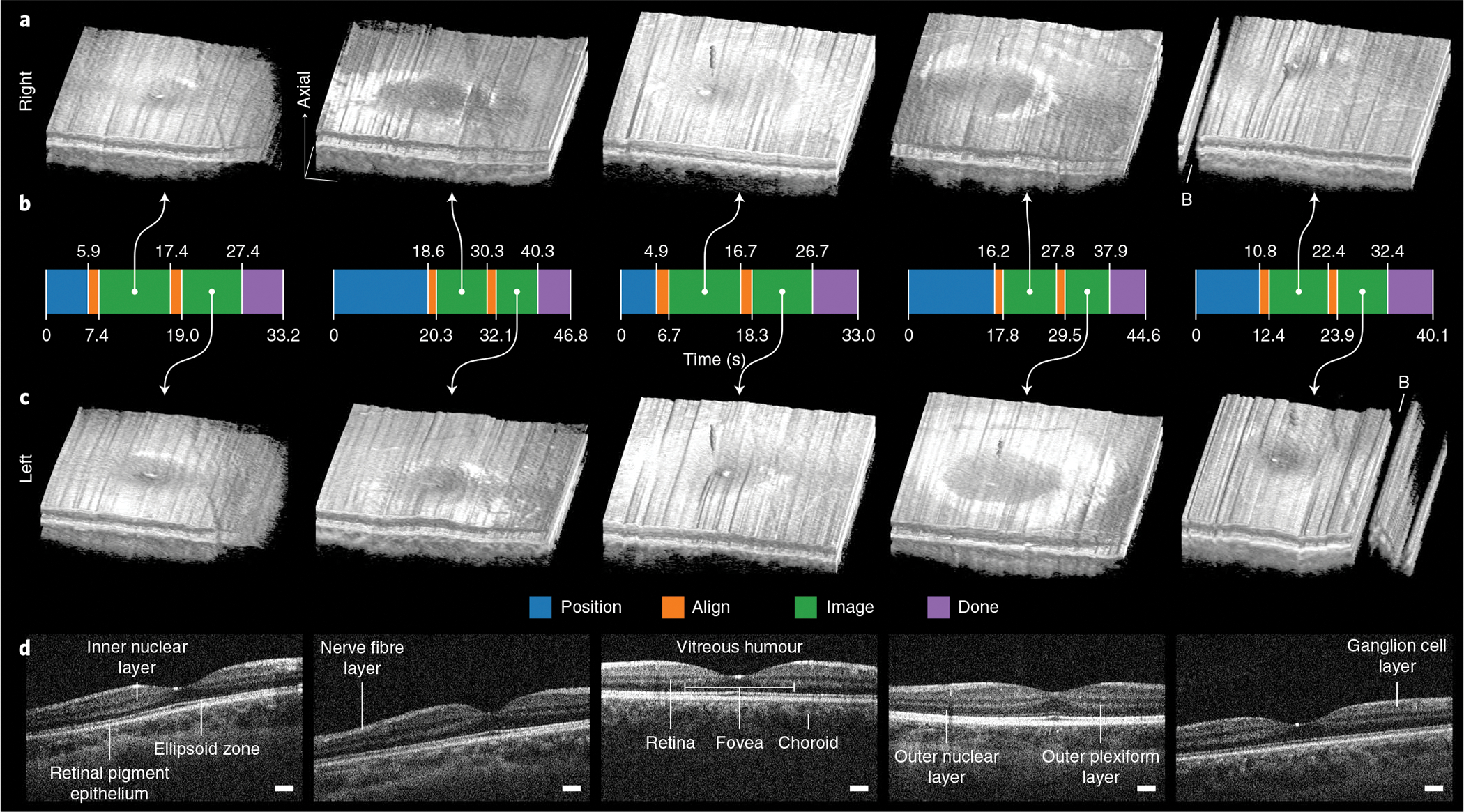
a,c, Right and left 800 × 200 × 1,376 voxel retinal volumes obtained with fully autonomous OCT imaging and registration in post-processing. These scans penetrate all retinal layers into the choroid and reveal the foveal pit within the surrounding parafoveal region. Volumes are axially stretched by a factor of two to reveal structure. Raw volumes are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2. B, artefacts from blink. b, Autonomous system mode from initial to last participant detection. For all participants, the system reliably performed 8–10 s of imaging per eye after aligning with the right and then the left eye with a total session time of under 50 s. The time required in advance to manually adjust the scan head for each participant’s eye defocus and length is not included. d, Un-averaged B-scans through the fovea for each of five participants (from left to right), revealing the fovea centralis, constituent retinal layers and underlying choroid. B-scans are axially stretched by a factor of three to reveal structure. Scale bars, 250 μm (laterally).
