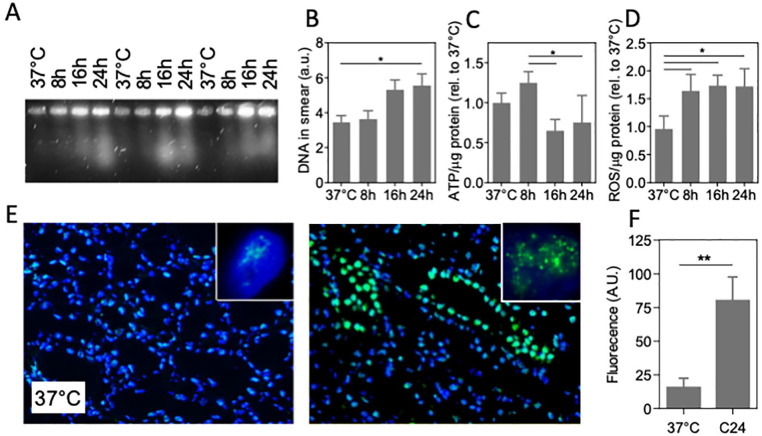
Figure 5.
DNA damage in cold-preserved porcine kidney. (A) Representative pulsed-field electrophoresis performed on pig kidney at 37°C and cooled kidney for 8, 16, and 24 h (4°C, UW preservation solution; three different kidneys shown). (B) Quantification of the amount of DNA in the PFGE smear. (C) ATP levels normalized to protein abundance. (D) Quantification of ROS levels assessed by MDA assay normalized to protein abundance. (E) Typical example of fluorescent staining of immunofluorescent staining of 53BP1 staining (green) of pig kidney tissue, showing abundant nuclear foci after 24 h cooling at 4°C. Nuclei are stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI;blue). Insets: representative single nucleus of a tubular cell. Original magnification: 100×. (F) Quantification of fluorescent intensity of 53BP1 staining. MDA: malondialdehyde; PFGE: pulsed-field gel electrophoresis; ROS: reactive oxygen species; UW: University of Wisconsin. C24 denotes cooling for 24 h; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.