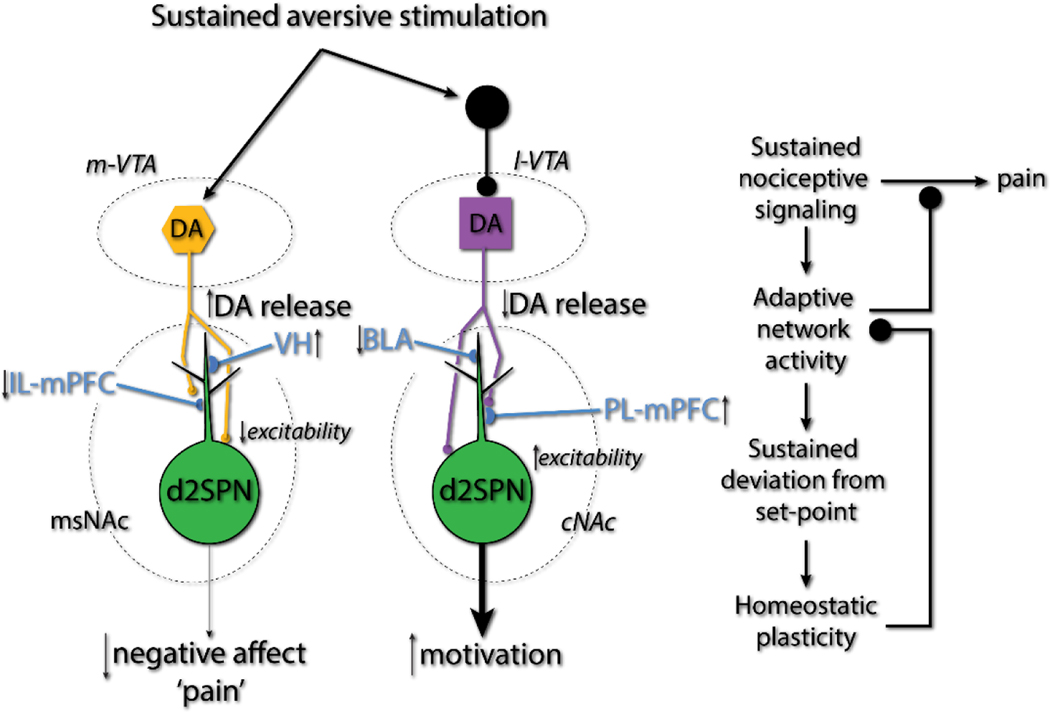
Figure 8. Schematic summarizing the adaptive synaptic and behavioral changes after pain induction.
Sustained aversive stimulation by SNI injury elevated the dopamine signaling in msNAc whereas decreased the dopamine in cNAc. This alterations of dopamine signaling in NAc appears to be adaptive – lessening the negative affect and enhancing the suppression of escape behavior, implying that cellular ‘homeostatic’ plasticity in NAc that comes with SNI is maladaptive at the network level, providing a novel therapeutic target for chronic pain.