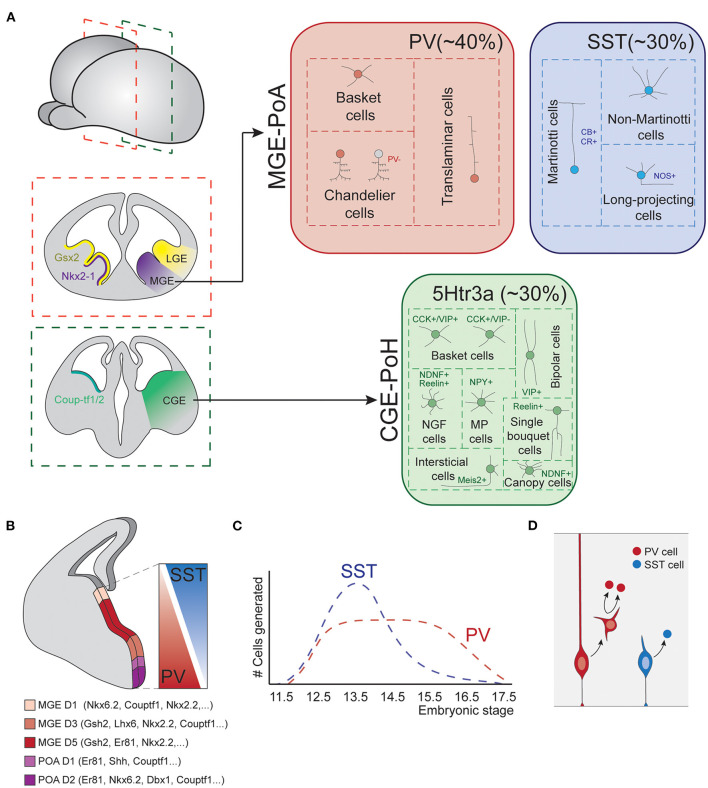
Figure 3.
Fate-specification of cortical interneurons. (A) The spatially organized expression of specific combinations of transcription factors subdivides the subpallium into different structures. Among those, the MGE and POA generate interneurons of both PV and SST classes. The CGE and POH are responsible for the generation of all types of 5Htr3a neurons. (B) MGE is further subdivided into spatial domains in the dorsoventral axis, each of these domains is defined by differential gene expression patterns. Such spatial patterning relates to the production of different interneuron types, as SST and PV cells largely derive from dorsal and ventral MGE respectively. (C) Temporal biases in interneuron origin. SST cells are mostly produced during early neurogenesis, while PV cell production remains nearly constant throughout the entire neurogenic window. (D) Progenitor cell mode of division also influences interneuron fates. Direct neurogenesis from apical progenitors mostly produces SST cells, while basal progenitor divisions mostly generate PV fates. MGE, medial ganglionic eminence; POA, preoptic area; CGE, caudal ganglionic eminence; POH, Preoptic-hypothalamic border domain; PV, parvalbumin; SST, somatostatin; CB, calbindin; CR, calretinin; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; CCK, cholecystokinin; VIP, vasointestinal peptide; NDNF, neuron derived neurotrophic factor; NPY, neuropeptide Y.