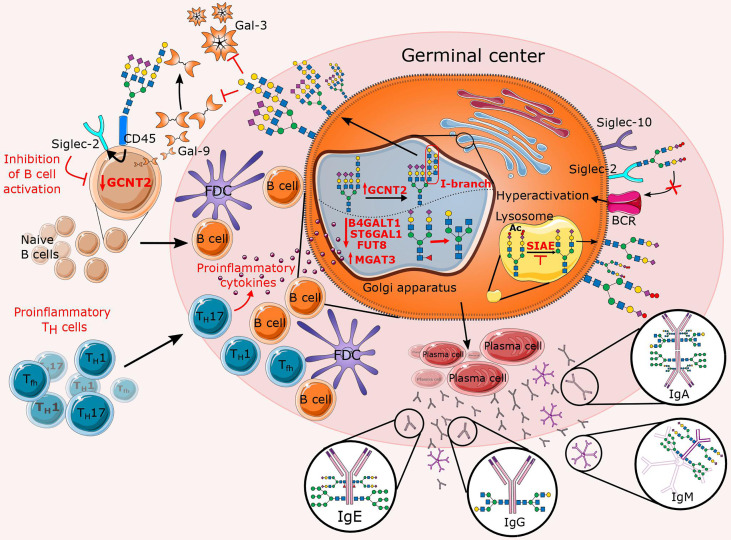
Figure 5.
Overview of altered N-glycosylation pathways regarding B cells during chronic inflammation. In the presence of proinflammatory stimuli, inflammatory T cells significantly affect B cell proliferation and their N-glycan profile by deregulating a specific subset of glycosyltransferases (B4GALT1, ST6GAL1, FUT8, MGAT3, and GCNT2). The latter is reflected in an increase in features such as bisecting GlcNAc, agalactosylation, afucosylation, and the presence of I-branches that have been shown to inhibit Gal-3 and Gal-9 binding. In addition to the affected Golgi enzymes, lysosomal sialic acid acetyl esterase (SIAE) is also downregulated so that it is unable to deacetylate sialic acids, which is necessary for immunomodulation of B cell receptor (BCR) signaling. This figure also summarizes the Fc N-glycome of secreted immunoglobulins, which reflects inflammation-related changes that may further contribute to disease progression.