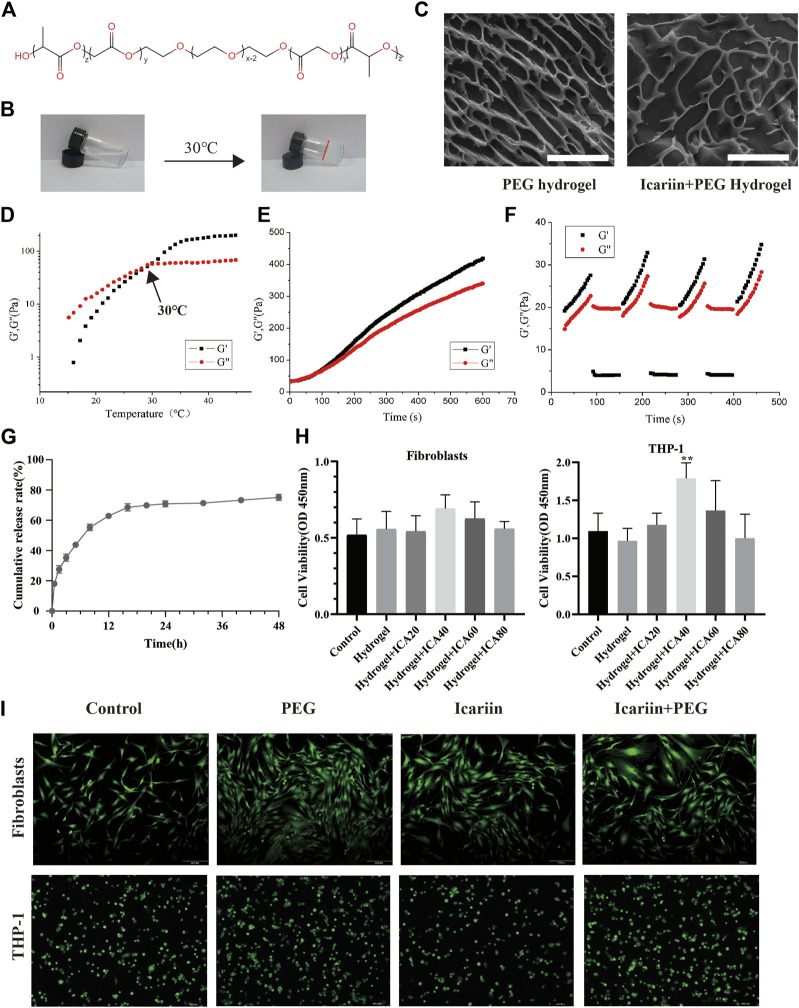
FIGURE 1.
Characterization and biocompatibility of the PEG hydrogel. (A) Chemical structure of the PEG hydrogel. (B) PEG hydrogel solution gelled at 30°C. (C) Cryo-scanning electron microscopy images of PEG and icariin+PEG hydrogels. Scale bar, 30 μm. (D) Temperature dependence of the storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G″) of the PEG hydrogel. (E) Gelation time of the PEG hydrogel at 35°C. (F) G′ and G″ of the PEG hydrogel when circulated three times between strain of 1 and 1,000%. (G) Release profile of icariin from the icariin+PEG hydrogel by UV spectrophotometry. (H) Cell viability on human fibroblast cells and THP-1 macrophages with hydrogel extracts of different compositions for 48 h. ICA20: 20 μg/ml icariin, ICA40: 40 μg/ml icariin, ICA60: 60 μg/ml icariin, ICA80: 80 μg/ml icariin, **p < 0.01 vs. the control. (I) Fluorescence microscopy of fibroblasts and macrophages was performed with live/dead cell staining. Live cells emit green fluorescence, while dead cells emit red fluorescence.