Figure 1.
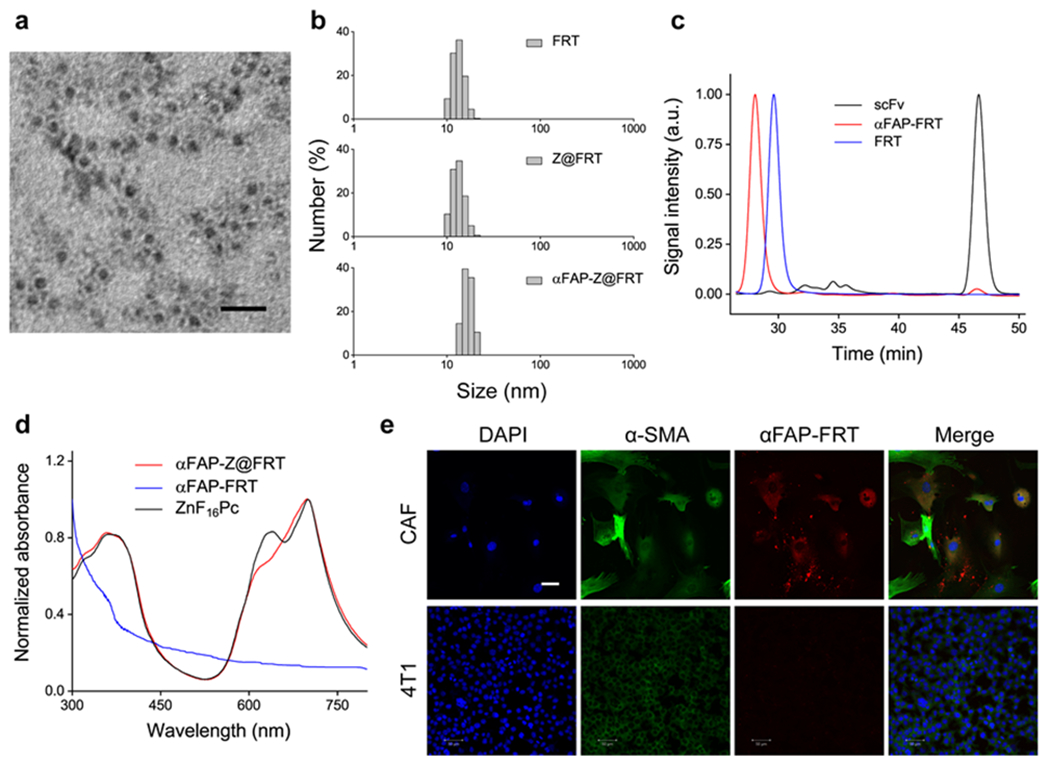
Characterizations of αFAP-Z@FRT. (a) TEM image of ferritin (FRT), with uranium acetate staining. Scale bar, 20 nm. (b) DLS analysis. The hydrodynamic sizes were 13.3 ± 2.0, 13.3 ± 2.1, and 16.8 ± 2.1 nm, respectively, for FRT, ZnF16Pc-loaded FRT (Z@FRT), anti-FAP-scFv-conjugated Z@FRT (αFAP-Z@FRT), in PBS (pH 7.4). (c) SEC analysis. The retention times (tR) were 28.1, 29.6, and 46.6 min, respectively, for αFAP-FRT, FRT, and scFv. (d) UV-vis analysis. The absorbance spectra of αFAP-Z@FRT, αFAP-FRT, and ZnF16Pc in PBS. For ZnF16Pc, 1% Tween 20 was added to the solution to improve solubility. (e) Confocal microscopy images. CAF and 4T1 cells were incubated with rhodamine-conjugated αFAP-FRTs for 12 h before taking images. Scale bar, 50 μm.
