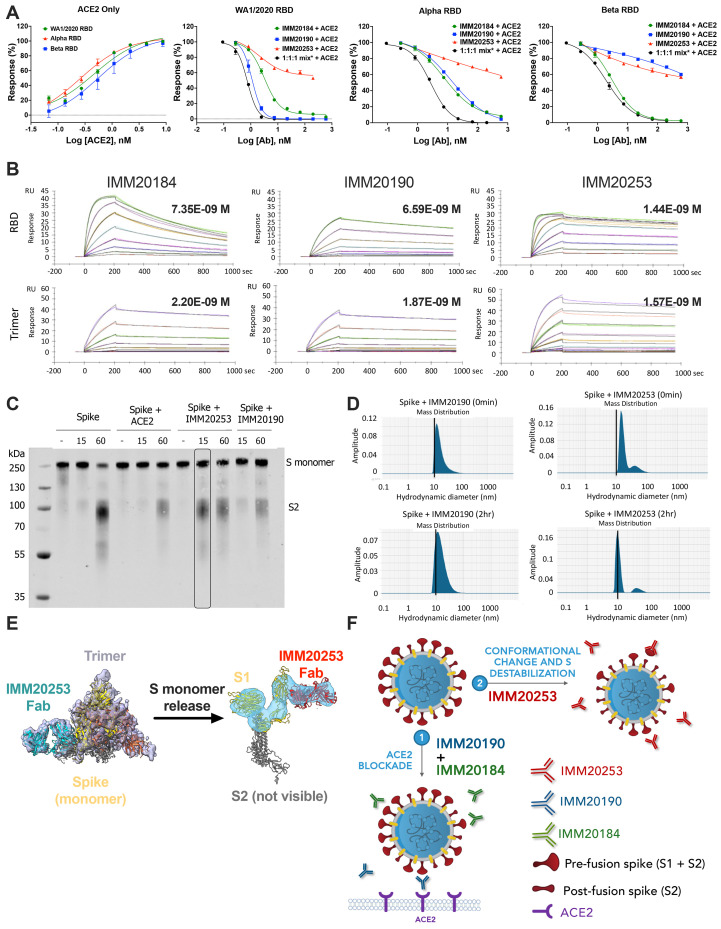
Fig. 5. IMM20253 antibody inhibits virus in non-ACE2 dependent manner and facilitates the release of S1 protein.
(A) Inhibition of RBD binding to its cellular receptor ACE2 in the presence of IMM20184/190/253. ELISA-based receptor competition assay. Denoted points are means of three replicates. Error bars denote SD. (B) Antibody binding kinetics of IMM20184, IMM20190 and IMM20253 antibodies to soluble RBD and Trimer (WA1/2020 variant) measured using Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR). Denoted values are KD. (C). Western blot analysis of Trimer digested with protease K after 0, 15 and 60 min in the presence of either human ACE2, IMM20253 or IMM20190. Anti-S2 staining reveals S monomer (S1+S2) and S2 protein. (D) Dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis of Trimer complex with IMM20253 or IMM20190 immediately or after 2 hours incubation measures a hydrodynamic diameter of each complex in nm. (E) IMM20253 Fab binding to Trimer triggers complex disruption and release of S monomers. (F) Schematic of mechanism of action of the IMM-BCP-01 cocktail.