Figure 2.
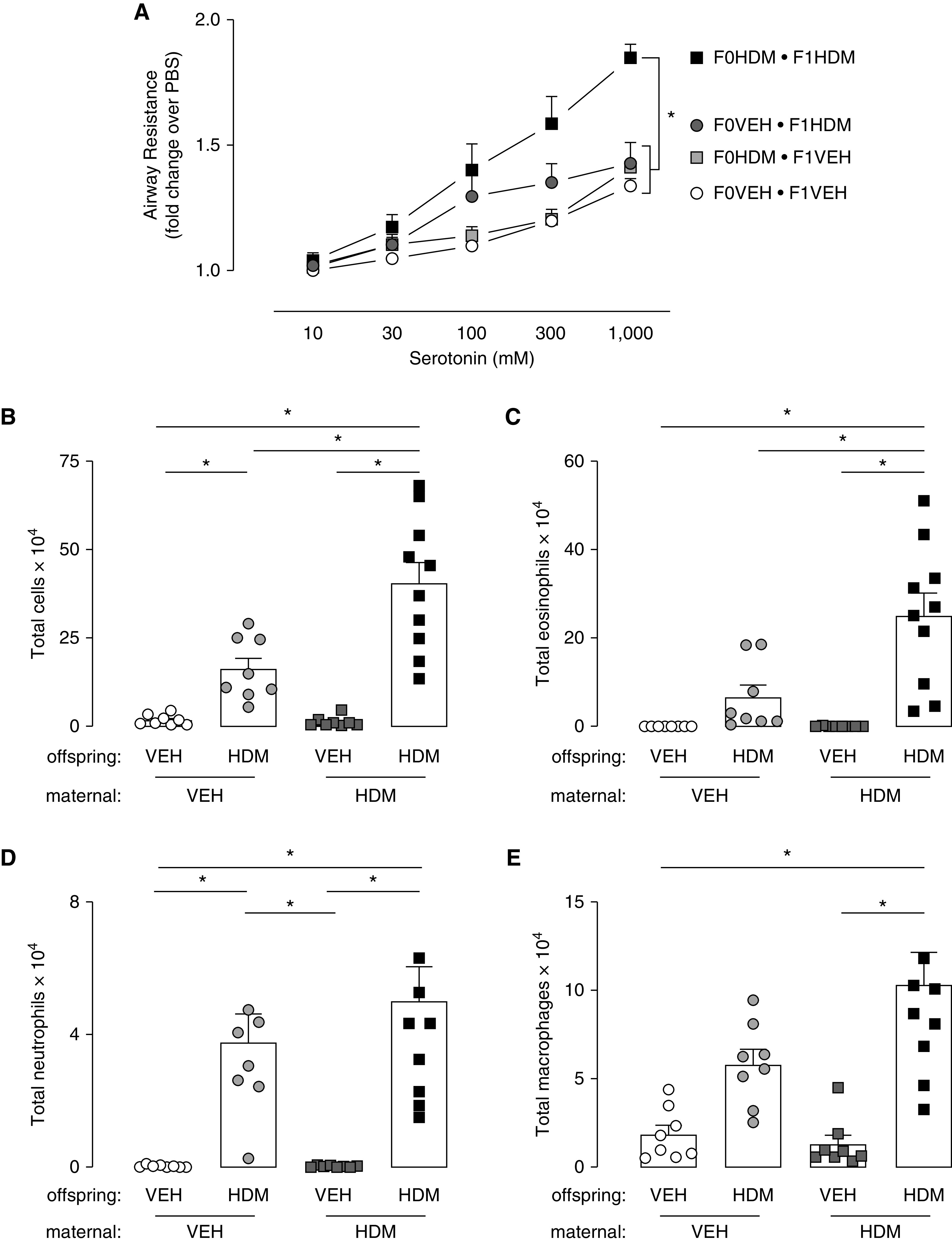
Maternal HDM exposure increased offspring airway hyperreactivity and inflammation. (A) Maternal HDM exposure did not change bronchoconstriction to inhaled serotonin in VEH-exposed offspring (VEH/VEH, open circles, n = 8; VEH/HDM, light gray squares, n = 8). Acute HDM sensitization and challenge caused airway hyperreactivity to inhaled serotonin in offspring compared with their VEH control mice independent of maternal treatment (VEH/VEH vs. VEH/HDM [dark gray circles, n = 8] and HDM/VEH vs. HDM/HDM [black squares, n = 10]). Allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity to serotonin was potentiated in offspring from HDM mothers (black squares) compared with VEH mothers (dark gray circles). (B) Airway inflammation increased in all offspring exposed to HDM compared with VEH control mice. (B and C) Maternal HDM exposure potentiated allergen-induced total (B) and eosinophilic (C) airway inflammatory cells in offspring. (D) Airway neutrophils and (E) macrophages increased in mice exposed to HDM compared to VEH control mice. *P < 0.05.
