Fig. 1.
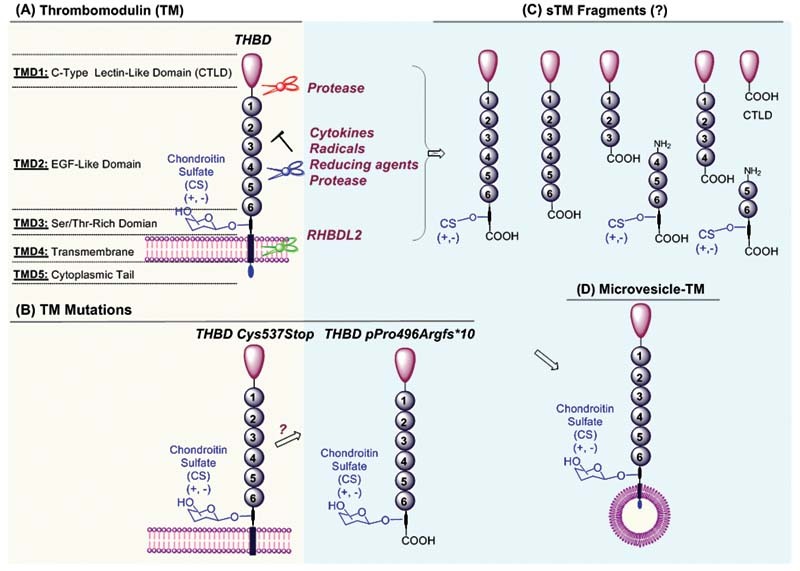
Schematic presentation of structural domains of membrane thrombomodulin (TM) ( A ) and TM mutations ( B ), its release mechanisms of predicted sTMs with corresponding domains (C), and microvesicle-TM ( C ). CS, chondroitin sulfate; CTLD, C-type lectin-like domain; EGF, epidermal growth factor; RHBDL2, the intramembrane protease rhomboid-like-2; Ser, serine; sTM, soluble thrombomodulin; Thr, threonine.
