Figure 5.
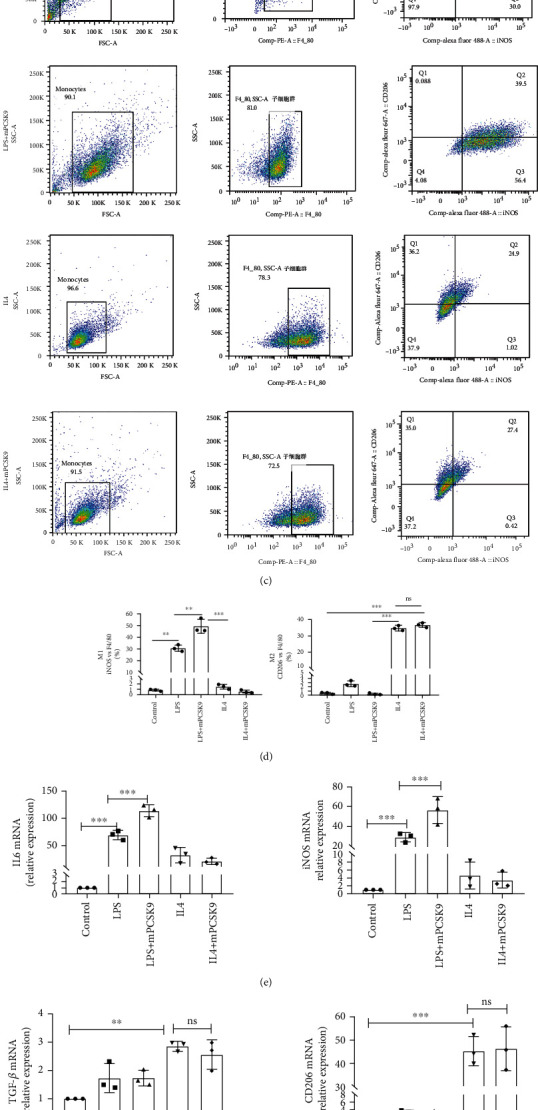
In vitro, the exogenous PCSK9 protein induced inflammatory macrophages to acquire the M1 phenotype. The morphologic changes in macrophages stimulated by LPS/IL4. Cell shape changed from round to fusiform in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells to ellipse in IL4-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Scale bar = 50 μm. (b) 0.5 μg/mL PCSK9 protein significantly induced IL6 expression in RAW264.7 and have no effect on cell viability. (c) Representative flow cytometry plots showing the percentages of M1 (F4/80+/iNOS+/CD206−) and M2 (F4/80+/iNOS−/CD206+) phenotype in LPS/IL4-stimulated RAW264.7 cells after cocultivation with PCSK9 protein for 24 h, n = 3. Pooled flow cytometry data from (c). (e, f) q-PCR analysis of IL-6, iNOS, TGF-β, and CD206 mRNA expression in LPS/IL4-stimulated RAW264.7 cells after cocultivation with PCSK9 protein for 24 h, n = 3. (g) Representative images of Western blots for IL6, iNOS, and TGF-β in LPS/IL4-stimulated RAW264.7 cells after cocultivation with PCSK9 protein for 24 h, n = 3. Protein levels of IL6, iNOS, and TGF-β of (g). ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001; ns: not significant.
