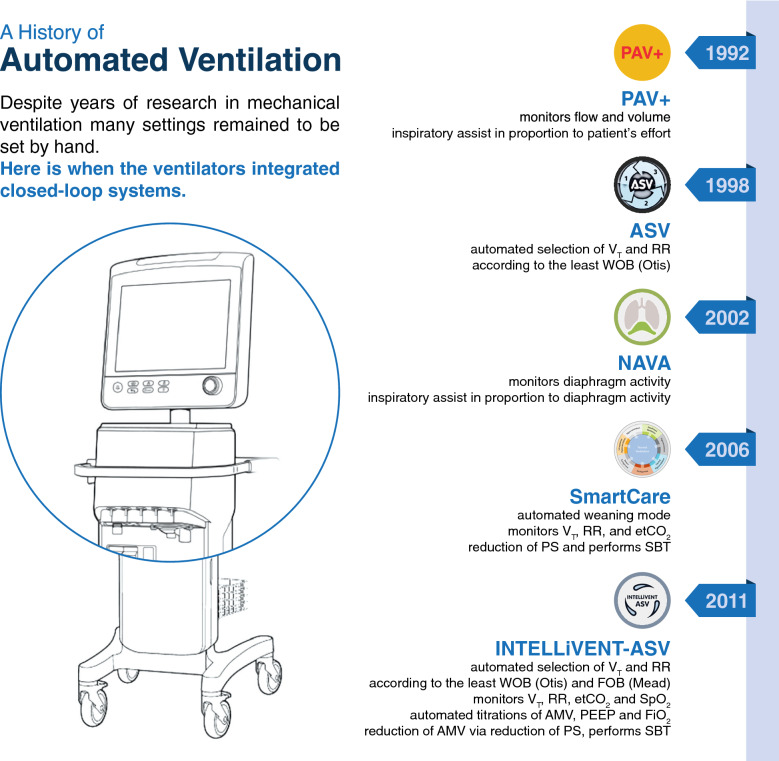
Fig. 1.
A history of automated ventilation. Overview of currently available closed–loop ventilation modes, with brief explanations of how they work. The here described examples of automated ventilation modes are Proportional Assist Ventilation with load–adjustable gain factors (PAV +), available on Puritan Bennett ventilators (Puritan Bennett, Minneapolis, USA), SmartCare, available on Dräger ventilators (Dräger, Lübeck, Germany), Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist ventilation (NAVA), available on Maquet ventilators (Getinge, Goteborg, Sweden), and Adaptive Support Ventilation (ASV) and its successor INTELLiVENT–ASV, available on Hamilton ventilators (Hamilton Medical AG, Bonaduz, Switzerland). Abbreviations: VT: tidal volume, RR: respiratory rate, etCO2: end-tidal carbon dioxide, PS: pressure support, SBT: spontaneous breathing trial, WOB: Work of Breathing, FOB: Force of Breathing, SpO2: pulse oximetry, FiO2: fraction of inspired oxygen