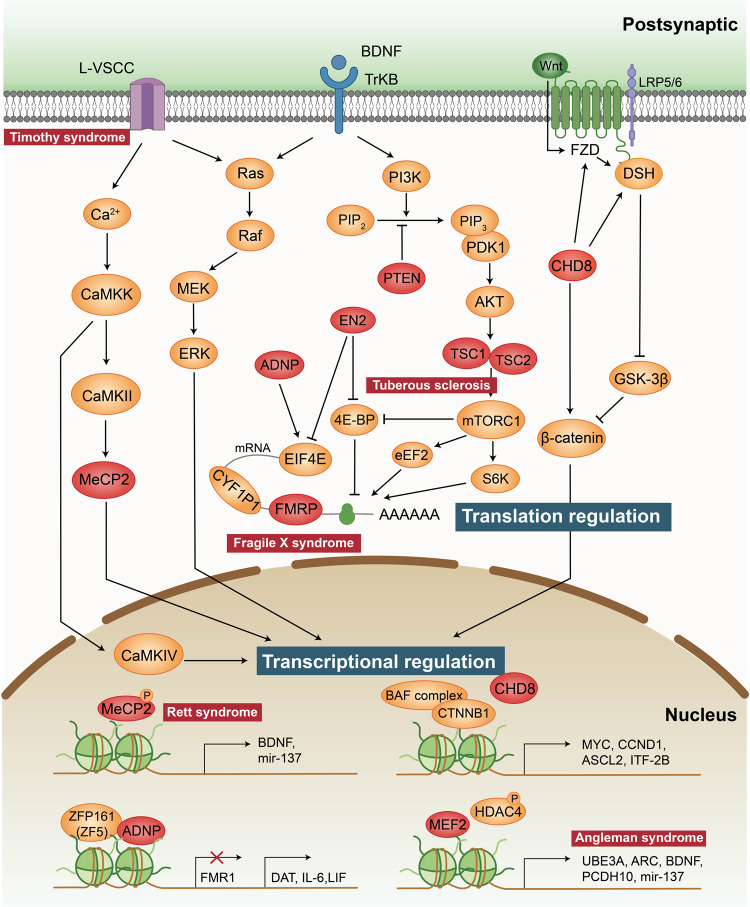
Fig. 3.
Transcription factors and translation mechanism associated with ASD. Activity-regulated translational pathways including the Ras/ERK and PI3K/mTOR. Both of them could be activated upon the stimulation of TrKB. Activation of L-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels (L-VSCCs) triggers calcium influx, induction of calcium-dependent signalling molecules and Ras/ERK pathways, involving in transcriptional regulation. These signalling cascades transcription regulators in the nucleus lead to the expression of transcription factors, thereby contributing to the regulation of activity-dependent gene transcription. Mutations of proteins involved in transcriptional regulation are associated with some syndromes of ASD, including L-VSCC in Timothy syndrome, MeCP2 in Rett syndrome and UBE3A in Angleman syndrome. Mutations of proteins involved in translation regulation including PTEN, ADNP, EN2, TSC1/TSC2 (tuberous sclerosis) and FMRP (fragile X syndrome). These genes have been highlighted in red