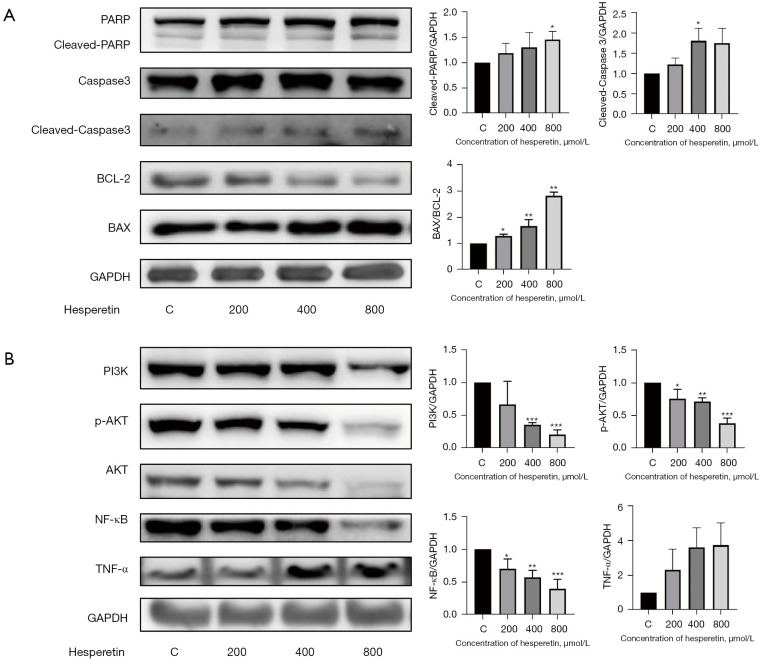
Figure 3.
Hesperetin might induce apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB pathways. (A) GL261 cells were treated with hesperetin at indicated concentrations for 24 h. Western blotting was used in detecting the expression of PARP, caspase-3, BCL-2, and BAX. Representative western blots show the expression of target proteins. Protein expression of cleaved-PARP and cleaved caspase-3 were quantified through densitometry and normalized to GAPDH. Protein expression of Bax was quantified through densitometry and normalized to BCL-2. One-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis (n≥3). *, P<0.05 and **, P<0.01 compared with the respective control group. (B) GL261 cells were treated with hesperetin at indicated concentrations for 24 h. Western blotting was used to detect the expression of PI3K, AKT, NF-κB, and TNF-α. Representative western blots present target protein expression. The protein expression of target proteins was quantified by densitometry and normalized to GAPDH. One-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis (n≥3). *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01, and ***, P<0.001 compared with the respective control group. C represents control group (without HSP treatment). PARP, Polyadenosine-diphosphate-ribose polymerase; Bcl-2, B cell lymphoma-2; BAX, BCL-2 associated X protein; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; p-AKT, phosphorylated -protein kinase B; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.