Figure 7.
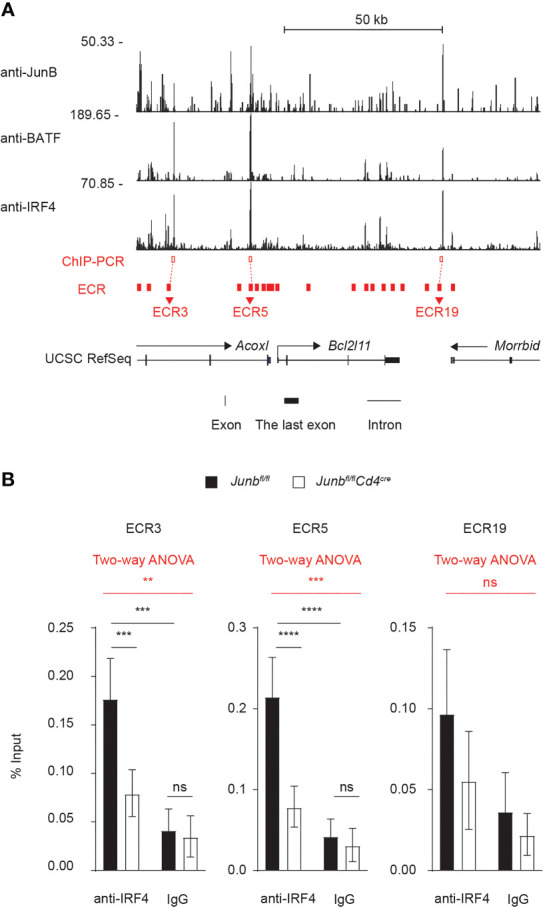
JunB is critical for IRF4 binding to the Bcl2l11 locus (A) Naive CD4+ T cells from Junbfl/fl mice were activated under Th1-polarizing conditions for 48 h and subjected to ChIP-seq analysis using JunB, BATF, and IRF4 antibodies. ChIP-seq peaks for JunB, BATF, and IRF4 on Bcl2l11 locus are shown. Three JunB/BATF/IRF4-colocalizing ChIP-seq peaks (red open box) were detected at regions close to evolutionarily conserved regions: ECR3, ECR5, and ECR19 of Bcl2l11 locus (red filled box). Transcription directions (arrows), transcription start sites (TSS, turn right arrows), exons (black vertical lines and boxes) and introns (black solid lines) are indicated. (B) Naive CD4+ T cells from control (Junbfl/fl ) or Junb-deficient (Junbfl/fCd4Cre ) mice were activated under Th1-polarizing conditions for 48 h and subjected to ChIP analysis using IRF4 antibodies. Eluted DNA was analyzed by qPCR using primers to detect genomic regions near ECR3, ECR5 and ECR19 (red open boxes shown in (A). Error bars indicate s.e.m (n = 6 wells per group). The significance of IRF4 binding on each genomic region was first tested by using two-way ANOVA, as shown on the top of each graph and highlighted in red. The difference lying on each group was tested by using Tukey test, as shown within each graph. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns non-significant (p > 0.05). Data represent a combination of two independent experiments.
