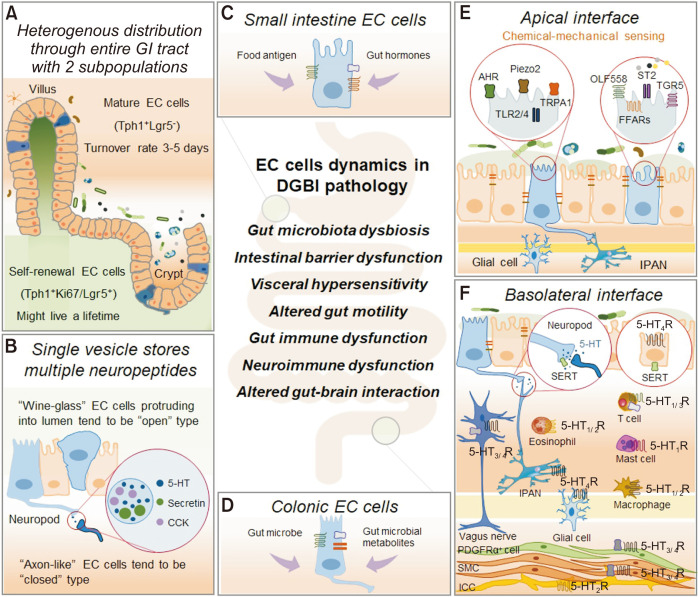
Figure.
Enterochromaffin (EC) cells dynamics in gut physiology and disorders of gut-brain interactions. (A) Heterogenous distribution of EC cells. (B-D) Functional heterogeneity of EC cells. Small intestine EC cells are specialized for sensing nutrients and colonic EC cells for gut microbiota and its derived molecules. (E, F) Apical and basolateral interface of EC cells. EC cells coordinate bilateral communication through crosstalk between dietary, microbial, and inflammatory factors to which their apical surface is exposed and to enteric neurons with afferent endings close to their basolateral surface, coordinating gut-brain communication. GI, gastrointestinal; Tph1, tryptophan hydroxylase 1; Lgr5, leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; CCK, cholecystokinin; DGBI, disorders of gut-brian interaction; AHR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; TRPA1, transient receptor potential ankyrin 1; TLR, toll-like receptor; OLF558, olfactory receptor 558; ST2, suppressing the tumorigenicity 2 receptor; TGR5, Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5; FFARs, free fatty acid receptor genes; SERT, serotonin reuptake transporter; 5-HTR, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor; IPAN, intrinsic primary afferent neuron; PDGFRα, platelet-derived growth factor receptor α; SMC, smooth muscle cell; ICC, interstitial cells of Cajal.