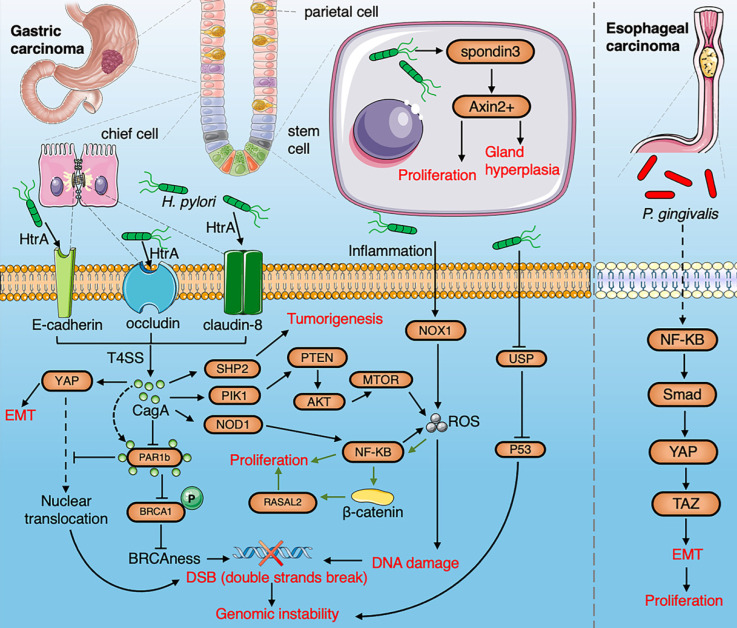
Figure 2.
A summarized figure demonstrating the linkage between the gut microbiome and gastric cancer and esophageal cancer. Section 1 Gastric cancer: HtrA protease secreted by H.pylori produce CagA protein by cleaving occludin, claudin-8 and E-cadherin. The cagA protein promotes EMT by activating the YAP pathway and inducing tumorigenesis through activation of NF-κB, PTEN, and SHP2 pathways. The production of ROS induced by H.pylori via the NF-κB pathway and inflammation contributes to DNA damage. H. pylori infection induces gastric stem cells to proliferate and stimulate gland hyperplasia through R-spondin 3 and Axin2. The interaction of CagA and PAR1b induces genomic instability by inhibiting the nuclear translocation of BRCA1 and YAP. The hypermethylation of USF1 by H. pylori degrades the p53 proteasome to promote gene instability. H.pylori-induced inflammation upregulates NOX1/ROS signaling pathway to promote the stemness of gastric cancer. H. pylori promotes the proliferation of cancer cell infection by activating the RASAL2/β-catenin signaling pathway. Section 2 ESCC: P. gingivalis trigger activation of NF-κB to induce EMT through the Smad/YAP/TAZ signaling pathway.