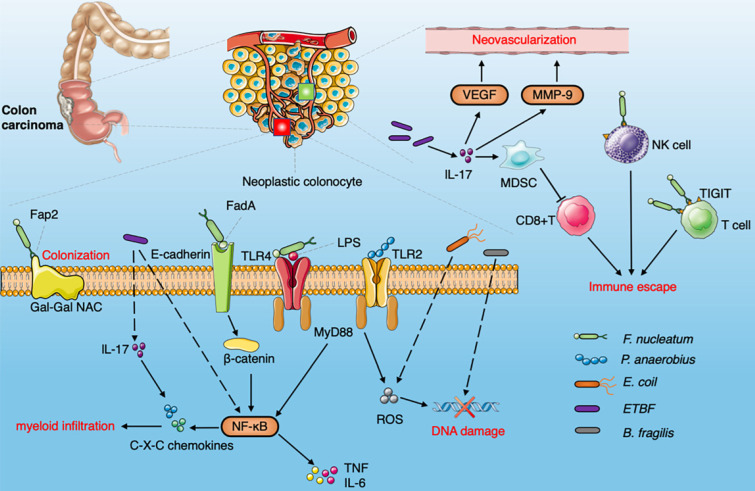
Figure 4.
Diagram summarizing the oncogenic interaction between the gut microbiome and CRC. The Fap2 protein combined with Gal-GalNAc is enriched on the surface of CRC cells to promote the colonization of F.nucleatum. F. nucleatum binds to E-cadherin on intestinal epithelial cells through FadA , activates the β-catenin signaling pathway, induces NF-κB pathway activation and upregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines, produces Fap2 to bind to TIGIT receptors on NK cells and other TILs. F.nucleatum activate NF-κB pathway via TLR4 and MYD88 to promote cell proliferation and invasion. Peptostreptococcus anaerobius increase the level of ROS via TLR2 and/or TLR4 signaling pathways. ETBF induce IL-17 and NF-κB pathway to enhance the production of C-X-C chemokine. MDSCs recruited by ETBF via IL-17 to inhibit the activity of cytotoxic CD8 + T cells. ETBF enhances the expression of MMP9 and VEGFA to induce neovascularization through IL-17. E. coli can also increase the level of ROS and promote the accumulation of spontaneous mutations. B. fragilis induces DNA damage.