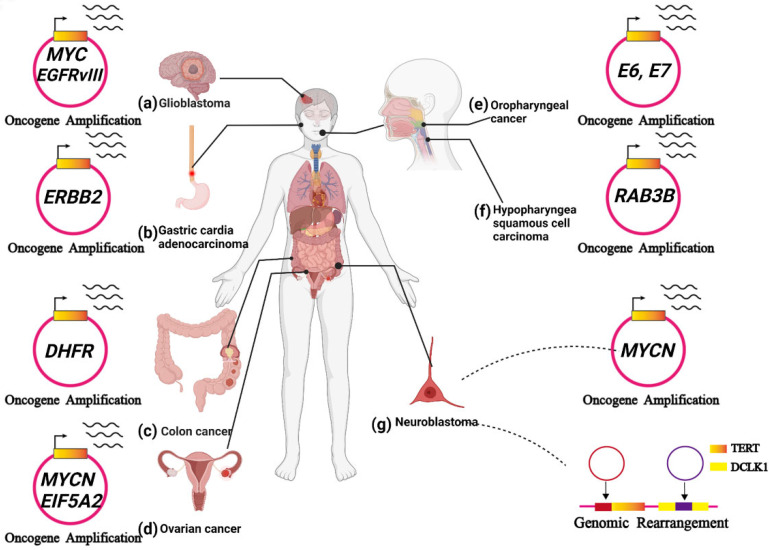
Figure 6.
ecDNA is related to tumour progression. (A) In glioblastoma, ecDNA initiates a great number of carcinogenic amplifications and mutations. (B) In gastric cardia adenocarcinoma, ecDNA-derived ERBB2 focal amplifications might serve as a prognostic biomarker. (C) In colon cancer, ecDNA-mediated gene amplification accounts for drug resistance. (D) In ovarian cancer, noncoding regions (MARs) on ecDNAs could enhance the expression of oncogenes near the MARs, including MYCN and EIF5A2. (E) In HPV-mediated oropharyngeal cancer: human-viral hybrid ecDNA could prompt oncogene expression and tumour evolution. (F) In hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma, the RAB3B gene was amplified on ecDNA, and RAB3B protein could induce a drug-resistant phenotype by promoting autophagy. (G) In neuroblastoma, ecDNA involves the amplification and rearrangement that contribute to tumorigenesis.