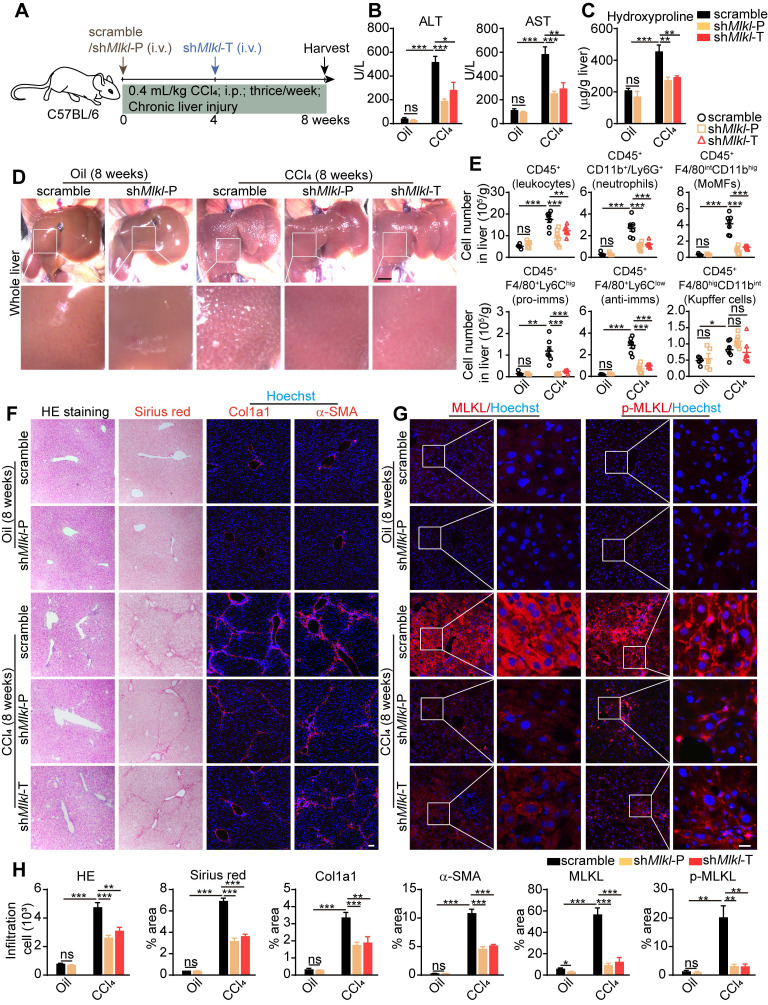
Figure 6.
AAV-shRNA mediated specific knockdown of Mlkl in hepatocytes reduces CCl4 induced liver fibrosis. (A) Schematic of the experimental design of AAV treatment in CCl4-induced fibrosis in mice. AAV-shMlkl was given in either preventative (shMlkl-P) or therapeutic (shMlkl-T) manner. (B) Serum ALT and AST in mice received AAV-shMlkl and CCl4 (Oil groups, n=5; CCl4 groups, n=7). (C) Hydroxyproline levels in the livers of mice received AAV-shMlkl and CCl4 (Oil groups, n=5; CCl4 groups, n=7). (D) Representative whole liver pictures of mice received AAV-shMlkl (or scramble sequence) and CCl4 (or vehicle)-treatment. Scale bar represents 0.5 cm. (E) Quantification of the numbers of total leukocytes, neutrophils, MoMFs, pro-imms, anti-imms, and Kupffer cells in the liver of mice received AAV-shMlkl and CCl4. (Oil groups, n=5; CCl4 groups, n=7). (F) Representative images of H&E and Sirius red staining, and immunofluorescence staining of Col1a1, α-SMA on liver sections. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342. (G) Representative images of immunofluorescence staining of MLKL or p-MLKL on liver tissue frozen sections. (H) Quantitative analysis of infiltration cells and positive staining areas in (F and G) (Oil groups, n=5; CCl4 groups, n=7. Data are shown as Means ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P< 0.001 (Student's t-test). Scale bar represents 100 µm.