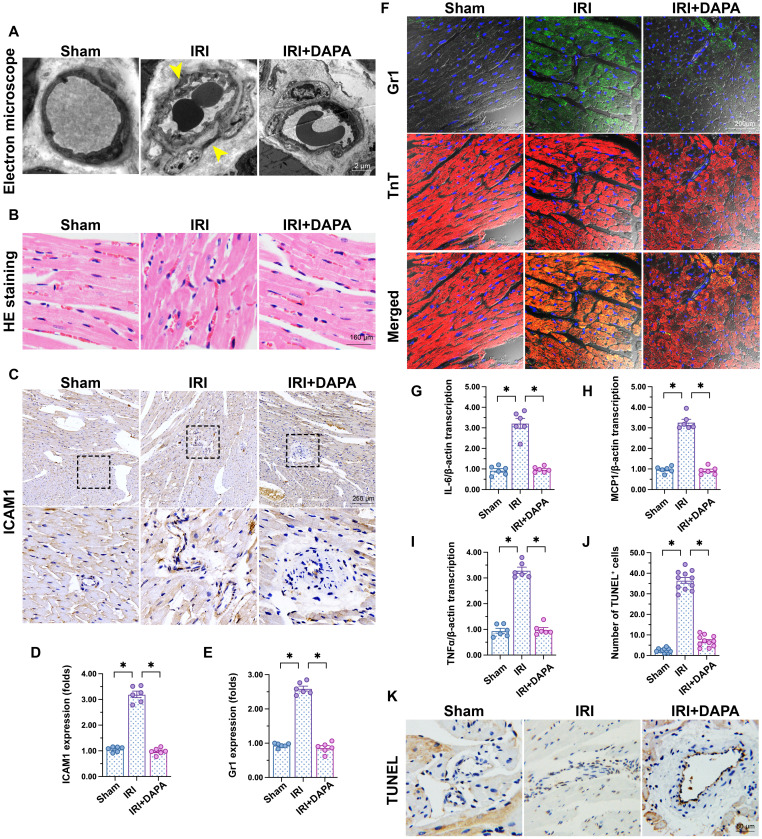
Figure 1.
DAPA attenuates IRI-induced microvascular injury. Mice were subjected to 45-min ischemia followed by 2-h reperfusion to induce cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI). Dapagliflozin (DAPA, 40 mg/kg/day) was administrated daily via intraperitoneal injection during seven days before IRI surgery. (A) Electron microscopy was used to detect ultrastructural alterations in the cardiac microcirculation. Yellow arrows indicate narrowed lumens and rough microvessel walls. (B) H&E staining was used to observe the morphology of erythrocytes in the cardiac microvasculature. (C, D) Immunohistochemistry was performed on heart tissues to detect the expression of ICAM1 on the surface of cardiac microvessels. (E, F) Immunofluorescence was used to detect intracardiac accumulation of Gr1+ neutrophils. Cardiomyocytes were stained with TnT and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. (G-I) The expression of IL-6, MCP1, and TNFα mRNA was determined by qPCR. β-actin was used as internal reference. (J, K) TUNEL staining was performed to detect and quantify apoptosis of cardiac microvascular ECs after IRI. Experiments were repeated at least three times and the data are shown as mean ± SEM. Six animals were used in each group and the dotes in each panel represent the average data of three replicates in each animal. *p < 0.05.