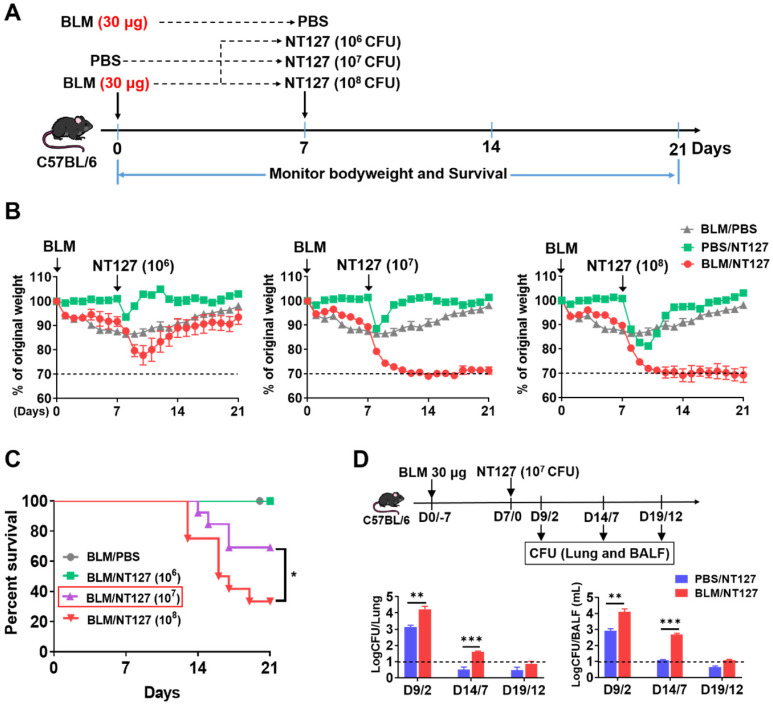
Figure 1.
Murine model of non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae NT127-infection-induced acute exacerbation of pulmonary fibrosis. (A) The workflow of animal modeling. BLM/NT127-treated mice were instilled intranasally with 30 μg BLM. After 7 days, the mice were infected intranasally with 106, 107 or 108 CFU NT127. The BLM-instilled and NT127-infected mice were used as controls. (B) Body weight changes in BLM-instilled, NT127-infected and BLM/NT127-treated mice. (C) Survival rates comparison among BLM-instilled mice and BLM/NT127-treated mice with 106, 107 and 108 CFU NT127. (D) Bacterial loads in murine lung homogenate and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid on 2, 7 and 12 days after NT127 infection. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments with nine or 10 mice in each group. Data shown as mean ± SEM. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. BLM: bleomycin.