Figure 1.
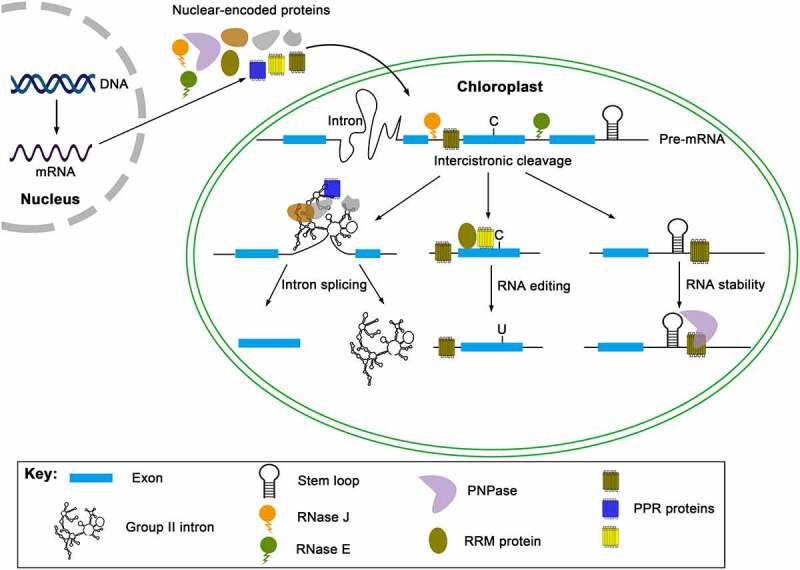
Post-transcriptional control of chloroplast gene expression in land plant chloroplasts. The post-transcriptional processing of chloroplast RNAs includes RNA cleavage of precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA), intron splicing, RNA editing, and RNA stability. Various nuclear-encoded proteins are implicated in these processes. RNase J and RNase E may act as endonucleases to cleave intercistronically. One or more sequence-specific RNA-binding proteins bind to intron RNA, and other splicing factors are recruited to intron RNAs, and the binding of these splicing factors assists the intron folding and splicing. The C-to-U editing is catalysed by PPR and RIP/MORF proteins, and a specific PPR protein targets an editing site by the cis sequence upstream of the editing site. The binding of RNA binding proteins can also protect RNA from exonucleolytic cleavage.
