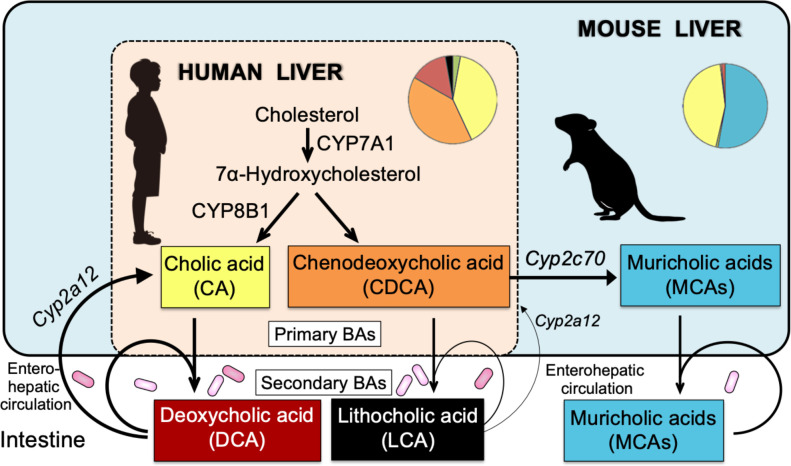
Fig 1. Comparison of bile acid (BA) metabolism between human and mouse.
CA and CDCA are end products in the human liver, but the mouse liver further metabolizes CDCA to MCAs by CYP2C70. In addition, the mouse liver can convert secondary BAs, DCA and LCA, into CA and CDCA by CYP2A12. Because of the low intestinal re-absorption rate (human and mouse) and small CDCA pool (wild-type mouse), the enterohepatic circulation of LCA is usually less (thin arrows) than those of other BAs (thick arrows). Knockout of the Cyp2a12 and Cyp2c70 genes results in mice with a human-like hydrophobic BA composition. Cyp2a12 and Cyp2c70 are genes responsible for hepatic BA 7α-hydroxylation and CDCA 6β-hydroxylation, respectively.