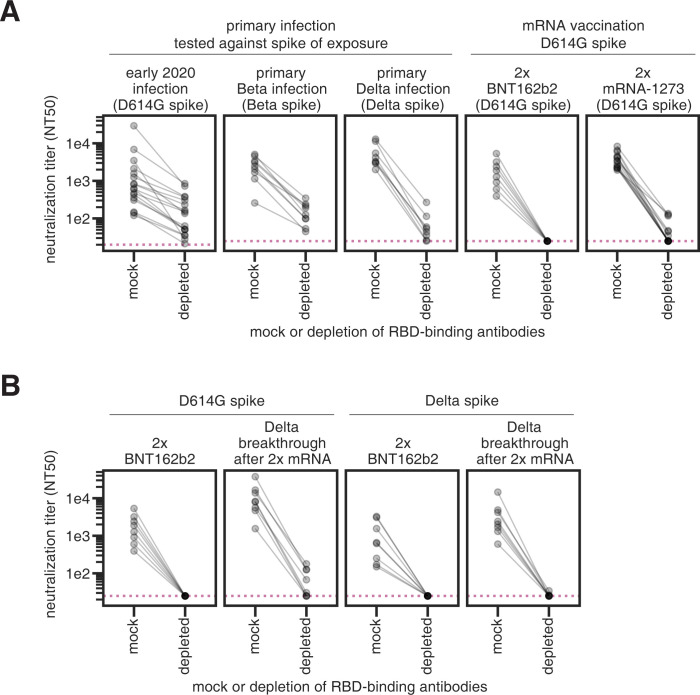
Fig 2. SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination elicits a neutralizing antibody response highly focused on the RBD.
(A) Plasma neutralization (neutralization titer 50%, NT50) against lentiviral particles pseudotyped with the homologous spike of exposure (in parentheses) following either mock depletion or depletion of RBD-binding antibodies for individuals who had primary infections with early 2020, Beta, or Delta viruses (and no prior SARS-CoV-2 infections or vaccinations), or individuals who completed the two-dose series of the mRNA vaccines BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 (labeled 2x BTN162b2 or 2x mRNA-1273). (B) Plasma neutralization following either mock depletion or depletion of RBD-binding antibodies for individuals who were vaccinated 2x with BNT162b2 or who had Delta breakthrough infections after 2x mRNA vaccination. Plasma samples were depleted of D614G RBD-binding antibodies and tested for neutralization against D614G spike (left), or depleted of Delta RBD-binding antibodies and tested for neutralization against Delta spike (right). In all cases, the RBD and spike from the same viral variant were used in both the depletions and neutralization assays. Note that the same 2x BNT162b2 data are shown in the right panel of (A) and in the left panel of (B) to facilitate visual comparison. The neutralizing titers for the early 2020 plasmas were first published in [23], the Beta plasmas in [12], and the 2x mRNA-1273 plasmas in [29]. The assays for the primary Delta infection, Delta breakthrough infection, and 2x BNT162b2, with both D614G and Delta RBD and spike were newly performed in this study. ELISAs that confirm depletion of RBD-binding antibodies performed in this study are in S1 Fig. The results new to this study are plotted by individual serum or plasma in S2 Fig. Full neutralization curves are shown in S7 Fig.