Figure 8.
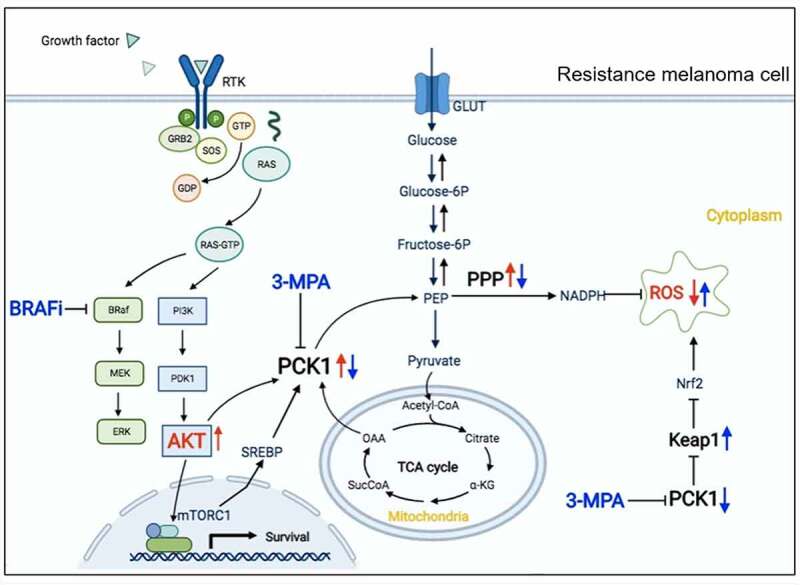
Mechanism of PCK1 and 3-mercaptopicolinic acid in resistant melanoma cells.
In resistant melanoma cells to b-Raf inhibitors, the AKT/PI3K signaling pathway is activated, which promotes the synthesis of PCK1 and phosphorylated PCK1. On the one hand, it mediates the upregulation of the PPP metabolic pathway, synthesizes a large amount of NADPH, reduces the intracellular ROS. On the other hand, it inhibits KEAP1, releases the restriction of Nrf2, and activates the antioxidant effect of cells. All of these will promote the acquired drug resistance. Combining with 3-MPA, the synthesis of NADPH by the PPP will decrease, and the antioxidant activity of cells will be inhibited, and then lead to the accumulation of ROS. As a result, 3-MPA can strengthen the killing effect by making oxidative attack to resistant melanoma cells.
