Figure 1.
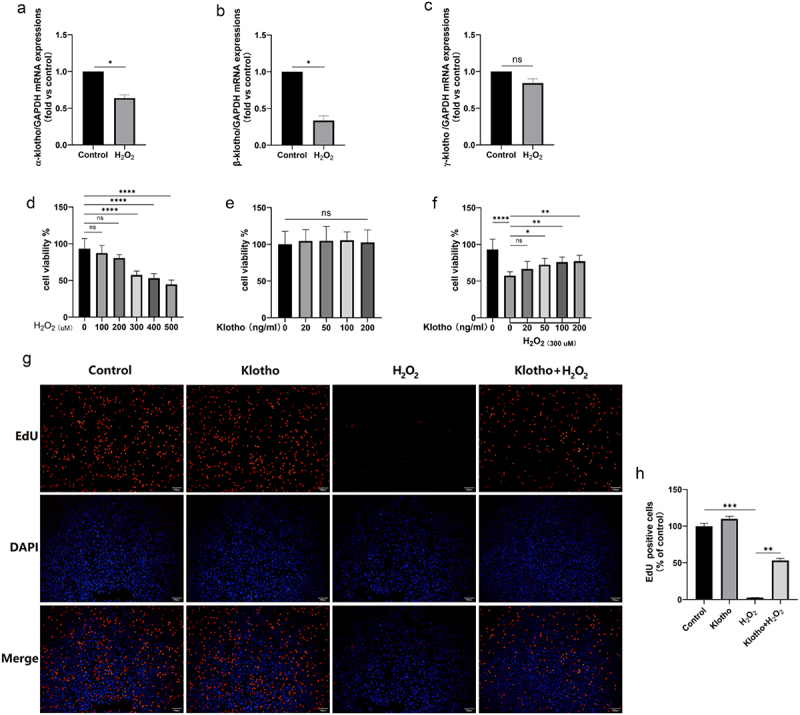
Klotho improved the inhibition H2O2-induced of ARPE-19 cells proliferation and H2O2 inhibited Klotho mRNA levels in ARPE-19 cells. (A, B, C) Real-Time qPCR was employed to determine the levels of α-, β- and γ-Klotho mRNA levels of ARPE-19 cells treated with H2O2 (300 µM) for 24 h. (d) CCK-8 assay was performed to detect the cell viability of ARPE-19 cells induced by H2O2 with different concentration (0–500 µM) for 24 h, (e) the cytotoxicity of Klotho (20–200 ng/ml) on ARPE-19 cells. ARPE-19 cells were incubated with or without Klotho (20–200 ng/ml) for 24 h then induced by H2O2 (300 µM) for 24 h. (f) the protective effect of Klotho on H2O2-induced injury of ARPE-19 cells was performed by CCK-8. ARPE-19 cells were incubated with or without Klotho (100 ng/ml) for 24 h then induced by H2O2 (300 µM) for 24 h. (g, h) The effect of Klotho pretreatment on the proliferation of H2O2-induced ARPE-19 cells detected by EdU assay. + indicates with treatment, – indicates without treatment. Each column presented means ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ‘ns’ represented no statistical significance.
