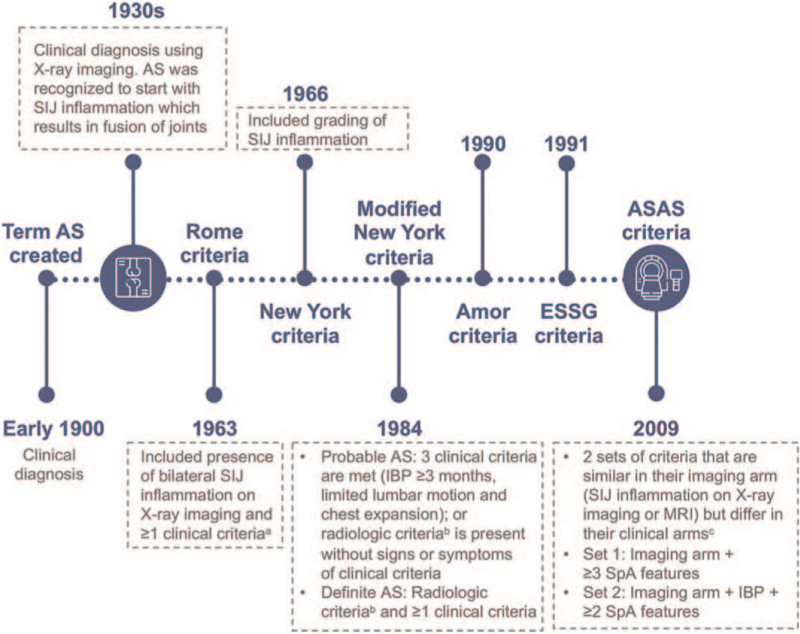
Figure 1.
Evolution of axSpA classification criteria. In the early 1900s, the term “AS” was created to describe the condition where there was inflammation in the spine and stiffness of all or part of the spine.[5] The use of X-ray imaging in the 1930s,[6] contributed to the creation of the 1963 Rome classification criteria of axSpA, 1966 New York classification criteria and then the 1984 modified New York classification criteria (where AS was probable or definitive depending on whether radiologic criteria was present and on the number of clinical criteria present).[7] Subsequently, the Amor classification criteria was introduced in 1990 and the ESSG classification criteria in 1991, preceding the ASAS classification criteria for axSpA in 2009, widening the scope of axSpA to include both AS and nr-axSpA.[1,2]aClinical criteria include: low back pain and stiffness >3 months; pain and stiffness in the thoracic region; limited lumbar movement; limited chest expansion; history or evidence of iritis or its sequelae; bSacroiliitis grade ≥2 bilaterally or sacroiliitis grade 3–4 unilaterally; cClinical arm includes the following SpA features: IBP, arthritis, enthesitis (heel), anterior uveitis, dactylitis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn disease/ulcerative colitis), good response to NSAIDs, family history of SpA, HLA-B27 positivity, and elevated CRP or ESR levels. AS = ankylosing spondylitis, ASAS = Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society, axSpA = axial spondyloarthritis, CRP = C-reactive protein, ESR = erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ESSG = European Spondyloarthopathy Study Group, HLA-B27 = human leukocyte antigen-B27, IBP = inflammatory back pain, MRI = magnetic resonance imaging, nr-axSpA = nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis, NSAID = nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug, SIJ = sacroiliac joint, SpA = spondyloarthritis.