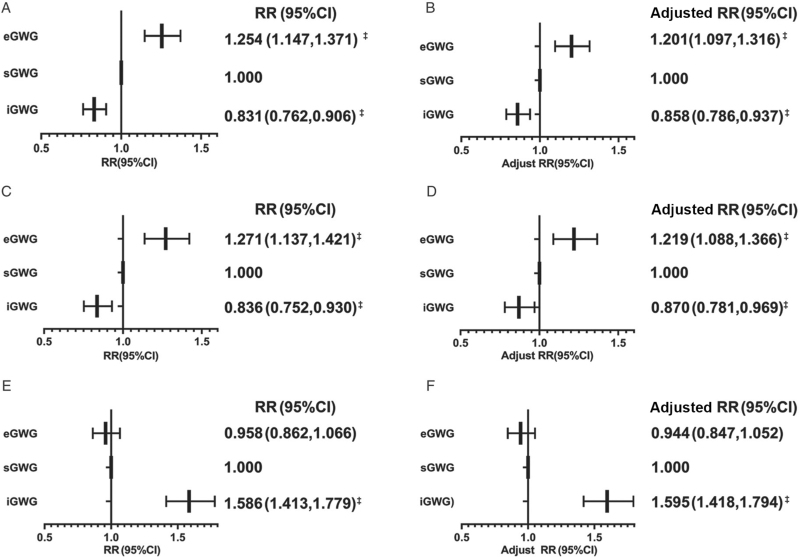
Figure 2.
Effect of GWG on GDM. (A) Effect of GWG-E on the risk of GDM. (B) Effect of GWG-E on the risk of GDM after adjustment. (C) Sensitivity analysis of the effect of GWG-E on the risk of GDM in the middle model. (D) Sensitivity analysis of the effect of GWG-E on the risk of GDM in the middle model after adjustment. (E) Effect of GWG-M on the risk of GDM. (F) Effect of GWG-M on the risk of GDM after adjustment. CI: Confidence intervals; eGWG: Excessive gestational weight gain; GDM: Gestational diabetes mellitus; GWG: Gestational weight gain; GWG-E: Gestational weight gain in early pregnancy; GWG-M: Gestational weight gain in middle pregnancy; iGWG: Insufficient gestational weight gain; RR: Relative risks; sGWG: Sufficient gestational weight gain. All models were adjusted for maternal age, ethnicity, assisted reproduction, gravidity, education, and employment. Logistic regression method: enter. ∗ P < 0.05, † P < 0.01, ‡ P < 0.001.