Fig. 7. Schematic representation of the roles of LSECtin in GC progression.
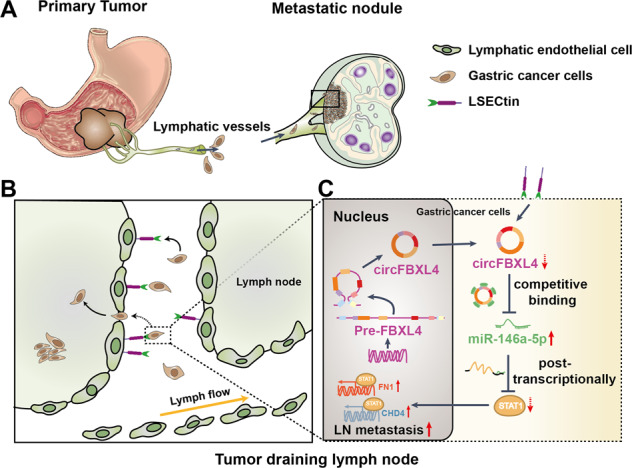
A GC cells infiltrate the surrounding tissues and lymphatic vessels, and reach the lymph nodes during lymphatic system metastases. B Under the action of molecules such as LSECtin, these cells adhere to the medullary sinus and subcapsular sinus, GC cells colonize to lymph nodes. C circFBXL4 can act through a ceRNA mechanism to “adsorb” miR-146a-5p to indirectly regulate the expression of STAT1, STAT1 affect the expression of FN1 and CHD4 as the transcription factor. LSECtin regulated STAT1, FN1 and CHD4 expression through the circFBXL4/miR-146a-5p axis, and affected the adhesion, proliferation, migration and invasion of GC cells, which might regulate GC lymphatic metastasis.
