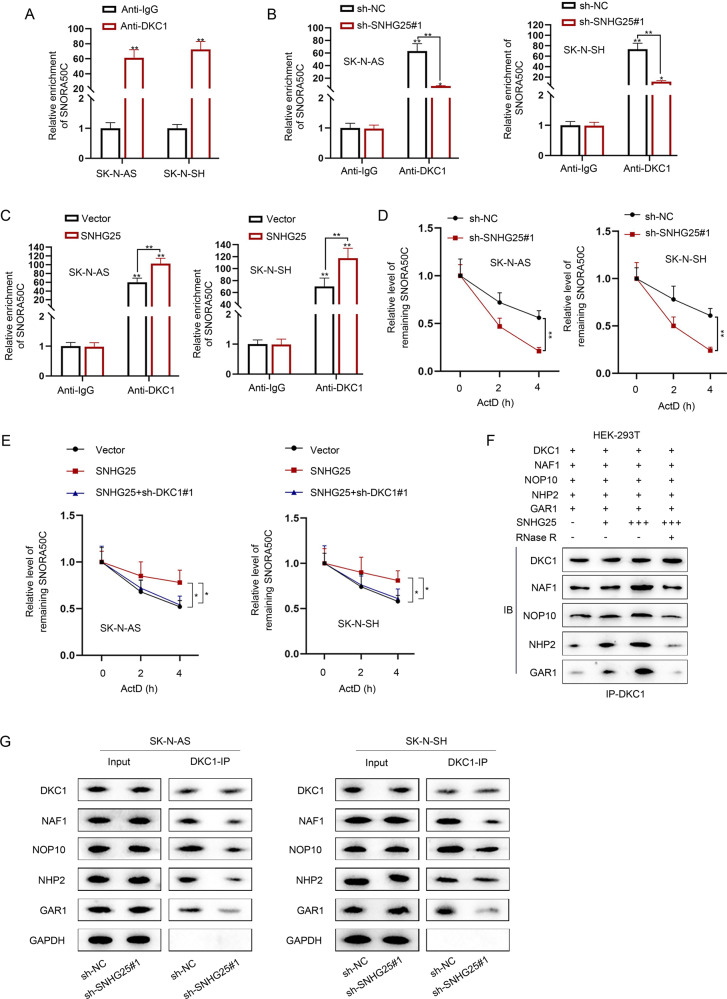
Fig. 5. SNHG25 relies on DKC1 to facilitate SNORA50C accumulation and associated snoRNP assembly.
A RIP assays detected the combination between DKC1 and SNORA50C in NB cells. (Student’s t-test) B, C RIP assays detected the combination between DKC1 and SNORA50C in NB cells with SNHG25 silence or overexpression. (Two-way ANOVA, Tukey) D ActD assay detected the stability of SNORA50C mRNA in SK-N-AS and SK-N-SH cells with SNHG25 silence. (Two-way ANOVA, Tukey) E ActD assay detected the stability of SNORA50C mRNA in SK-N-AS and SK-N-SH cells transfected with vector, SNHG25 and SNHG25 + sh-DKC1#1. (One-way ANOVA, Dunnett) F Co-IP assay detected the binding of DKC1 and other snoRNP-related proteins (NAF1, NOP10, NHP2, and GAR1) in the presence of SNHG25 and RNase R. G Co-IP assay detected the binding of DKC1 with NAF1, NOP10, NHP2, and GAR1 in SK-N-AS and SK-N-SH cells with SNHG25 deficiency. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Error bars indicate mean ± SD. (N = 3).