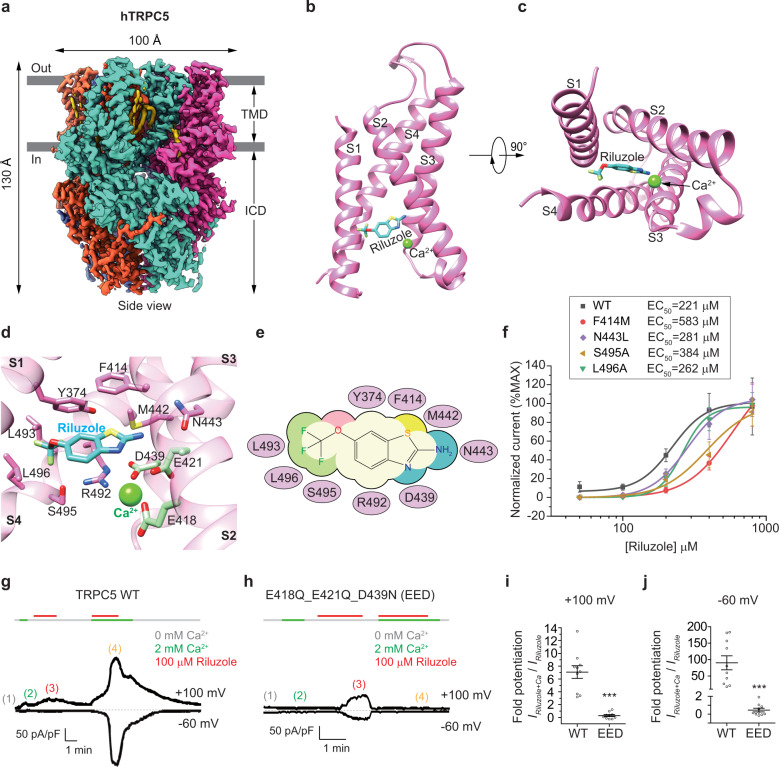
Fig. 1. Structure of the hTRPC5 channel in complex with riluzole.
a The cryo-EM density map of riluzole-bound hTRPC5 shown in side view. Four subunits are colored in hot pink, cyan, orange and blue, respectively. Lipids are colored in yellow. The cell membrane is indicated by gray lines. TMD, transmembrane domain; ICD, intracellular cytosolic domain. b, c Overview of the riluzole-binding site in hTRPC5. Riluzole is shown as sticks and colored in light sea green. Ca2+ ion is shown as a green sphere. Side view (b) and bottom view (c) are shown. d Close-up view of the riluzole-binding site and Ca2+-binding site. The main chains of hTRPC5 are shown as cartoons and colored in transparent hot pink. Side chains of interacting residues are shown as sticks. Residues colored in hot pink and D439 interact with riluzole. And residues colored in light green interact with Ca2+. e Cartoon representation of the interaction between riluzole and hTRPC5. Interacting residues are labeled in the purple ovals. f The activation effects of riluzole on various hTRPC5 mutants, measured by electrophysiological recordings under 0 mM extracellular Ca2+ at −100 mV. Representative traces are shown in Supplementary Fig. S3. Recordings from at least 10 cells were analyzed for each mutant. Data were fitted by dose-response curves and were normalized to ‘max currents’ (the maximal response produced by the drug). Data are shown as means ± SEM. g, h Ca2+-dependent potentiation of riluzole-activated TRPC5 currents of wild-type (WT) (g) and TRPC5_E418Q_E421Q_D439N mutant (EED) (h). TRPC5 currents were elicited by 2 s voltage ramps from −60 mV to +100 mV, applied at 0.33 Hz from a holding potential of −60 mV. The currents at +100 mV (the steady currents of 500 ms step of +100 mV at end of ramp, top trace) and −60 mV (the steady currents of 100 ms step of −60 mV before ramp, bottom trace) are plotted. Stimuli of 2 mM extracellular Ca2+ (marked as green lines) and 100 μM riluzole (marked as red lines) were individually or synergistically applied to cells. Basal condition of 0 mM extracellular Ca2+ is marked as gray lines. Representative ramp traces at basal state (0 mM Ca2+, marked with 1 and colored in gray), 2 mM Ca2+ (2, in green), 100 μM riluzole in 0 mM Ca2+ (3, in red), and 100 μM riluzole in 2 mM Ca2+ (4, in yellow) are shown in Supplementary Fig. S4 for comparison. i, j Statistical summaries of the fold potentiation of riluzole-activated current at +100 mV (i) or −60 mV (j) in 2 mM Ca2+ external relative to 0 mM Ca2+ external. n = 10 cells for each column. Data are shown in means ± SEM. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test was calculated for (i) and (j) with criteria of significance; ***P < 0.001.