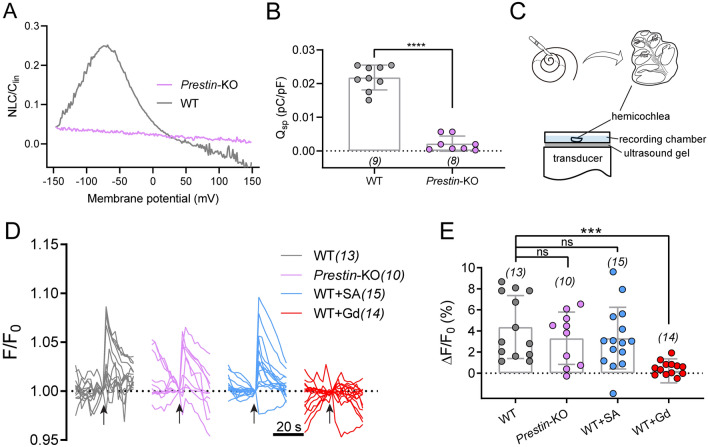
Fig. 5.
Ultrahigh-frequency-induced response in cochlear OHCs after Prestin deletion. A Nonlinear capacitance (NLC) in both Prestin-knockout and WT control OHCs. A representative example showing typical NLC pattern from a control OHC (gray). The NLC is absent in Prestin-knockout OHCs (purple). B Qsp (Qmax/Clin) in Prestin-KO and WT OHCs. Unpaired t-test, ****P <0.0001. C Schematic showing preparation of hemicochlea and setup for ultrasonic transducer stimulation. An 80-kHz transducer is fixed underneath the recording dish with ultrasound gel. D Ultrasonic stimulation evokes Ca2+ responses in OHCs of cochlea preparations from control and Prestin-KO mice. WT cochleae, Prestin-KO cochleae, WT cochleae treated with 10 mmol/L salicylic acid (WT+SA) were examined for the blockade of Prestin, and WT cochleae were treated with 10 μmol/L Gd3+ (WT+Gd). Arrows indicate ultrasonic stimulation. The images were collected at 2-s intervals. E Quantification of the peak Ca2+ responses of OHCs calculated from recordings in (D). Kruskal-Wallis test: WT vs Prestin-KO, P >0.9999; WT vs WT+SA, P >0.9999; WT vs WT+Gd, ***P = 0.0001. In (B) and (E), data are presented as the mean ± SD, and N numbers are shown in panels.