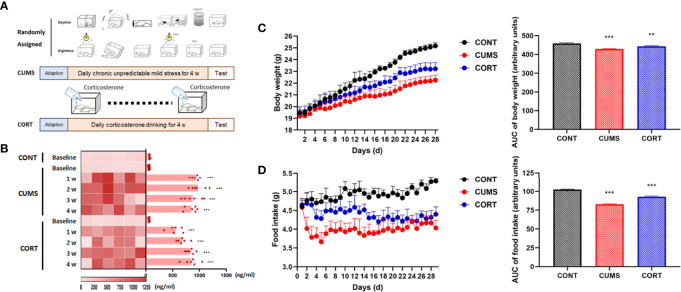
Figure 1.
Mice with chronic stress exhibited negative effects on daily weight gain and stress. (A) Mice in chronic stress received CUMS or CORT drinking for 4 weeks. (B) Serum CORT level was measured at baseline, 1, 2, 3, and 4 weeks after receiving chronic stress (repeated measurement ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, ***P < 0.001, compared with baseline; n = 6). (C) Daily body weight was recorded and area under the time-course curve (AUC) was analyzed (two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared with CONT; n = 12). (D) Daily food intake was recorded and AUC was analyzed (two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, ***P < 0.001, compared with CONT; n = 12).