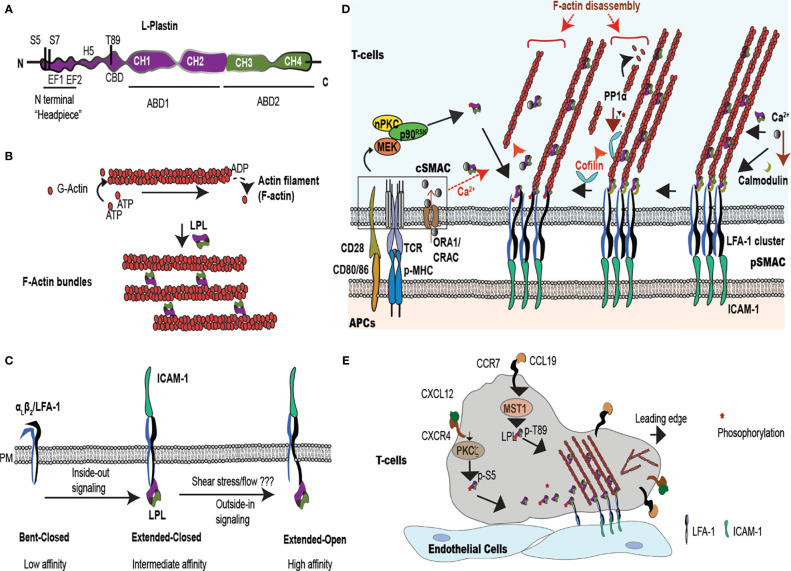
Figure 1.
LPL is an actin-bundling protein that supports T cell synapse maturation and migration. (A) LPL comprises a regulatory ‘N-terminal headpiece’ and two actin binding domains (ABDs). The regulatory headpiece includes three known phosphorylation sites (Ser-5, Ser-7, Thr89), two calcium binding EF domains, a regulatory H5 “switch helix,” and a calmodulin binding domain (CBD). (B) LPL cross-links two actin filaments to generates f-actin bundles. (C) LPL interacts with the cytoplasmic tail of the β2 subunit of the integrin LFA-1. In T cells, inside-out signaling induces a conformational change from low to intermediate affinity, whereas shear flow or ICAM-1 engagement triggers the high-affinity, extended-open conformation. (D) Multiple regulatory pathways converge upon LPL in the pSMAC, where LFA-1 mediates tight approximation to ICAM-expressing APCs. The IS, the interface at the site of T-cell:APC contact site, generates a cSMAC, pSMAC and a dSMAC (dSMAC not shown). In the IS, TCR ligation to peptide-loaded MHC (pMHC) and costimulatory CD28:CD80/86 interactions occur in the central super-molecular activation complex (cSMAC), which activates a kinase cascade [nPKC-MEK- ribosomal protein S6 kinase p90 (p90RSK)]. This kinase cascade results in Ser-5 phosphorylation of LPL. LPL phosphorylation accelerates LFA-1 clustering in the peripheral SMAC (pSMAC). Phosphorylated LPL is largely associated with high affinity LFA-1, and may stabilize the IS. LPL can also bind to LFA-1 independently of phosphorylation. LPL-induced LFA-1 clusters further accumulate at IS by cofilin-mediated f-actin remodeling. Cofilin is activated by PP1α phosphatase. Simultaneously, LPL also recruits f-actin bundles to connect the IS to actin cytoskeleton. Ca2+ influx at cSMAC also regulates LPL. Ca2+ binding reduces the LPL bundling efficiency, perhaps allowing f-actin clearing at IS. However, lower Ca2+ in the pSMAC permits calmodulin binding to LPL, stabilizing actin bundles and maintainting LFA-1 clustering. (E) Intravascular T cells traffic to peripheral immunological sites via the binding of the integrin LFA-1 to the adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, expressed on vascular endothelial cells. In response to chemoattractants, such as CXCL12 and CCL19, T cells polarize the respective chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CCR7 to the leading edge and activate kinases such Mst1 and PKCζ. Mst1, PKCζ, and other kinases phosphorylate the regulatory headpiece of LPL. Phosphorylated LPL initiates LFA-1 clustering, sustaining ICAM-1 binding. Branched f-actin forms in the lamellipod, while the ‘uropod’ propels cells in a forward direction. The symbol "*" indicates the phosphate group during phosphorylation/dephosphorylation reaction.