Figure 1.
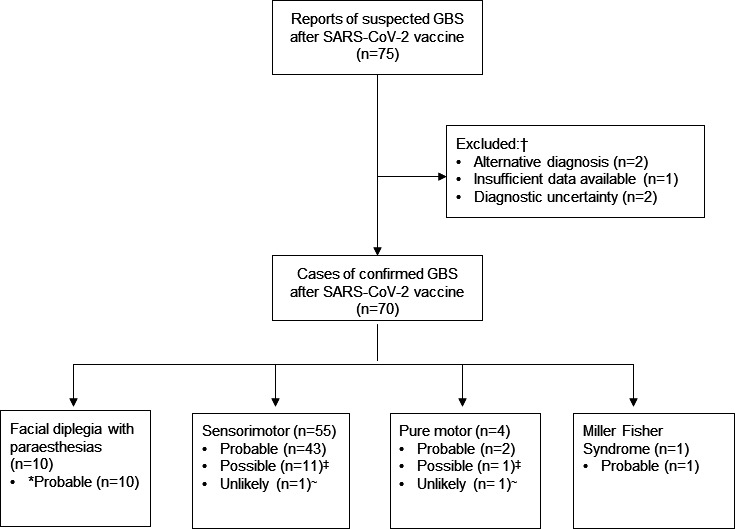
Study flow chart showing clinical variants of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) and levels of certainty of a link to the vaccine, as determined by the modified WHO Causality Assessment. *Levels of certainty of a link to the vaccine, as determined by the modified WHO Causality Assessment.20 †The five excluded cases comprised one with insufficient data, two with alternative diagnosis (neurosarcoidois and CIDP) made subsequently by the treating clinicians and two rapidly fatal cases that had features inconsistent with GBS and were excluded following discussions with the independent assessors. One of these two cases had upgoing plantars, normal CSF protein and no imaging or nerve conduction studies performed prior to death. The second case had normal CSF protein but raised white cell count and widespread demyelination on brain and spinal MRI. ‡Reasons for categorisation as ‘possible’ (n=12) included: antecedent infection without a recognised microbiological trigger for GBS ((n=5): URTI (n=2), IECOPD (n=1), Klebsiella urinary tract infection (n=1), gastroenteritis with no suspicion of Campylobacter and in unlikely temporal association with GBS (n=1)),53 raised C reactive protein without infective symptoms (n=1), use of small molecule inhibitors anecdotally associated with GBS (n=1),56 presence of systemic disease that might cause GBS-mimicking neuropathy ((n=3): CLL with acute axonal neuropathy (n=1)57 and MGUS with AIDP (n=1),58 suspected endocrinopathy and functional neurological overlay (n=1)), overlay with subacute demyelinating neuropathy (n=1), event occurring between 6 and 12 weeks from vaccination (n=1). ~Reasons for categorisation as ‘unlikely’ included microbiological evidence or clinical suspicion of Campylobacter jejuni infection (n=2). AIDP, acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy; CIDP, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; IECOPD, infective exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; MGUS, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance; URTI, upper respiratory tract infection.
