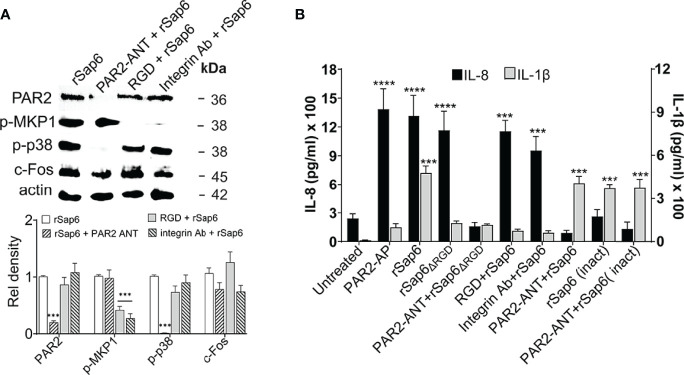
Figure 5.
Sap6 RGD domain is required for IL-1β release independent of PAR2 activation while IL-8 release is PAR2 dependent. OECs were treated with rSap6, rSap6ΔRGD or rSap6 (Inact) (all at 10µM) or pretreated with PAR2-ANT (100µM), RGD peptide (10µM) or ant-integrin Ab (1:100) for 3 h (for MAPK signaling) or 24 h (for cytokine release in culture supernatants). (A) Immunoblotting and densitometry showed that pretreatment with PAR2-ANT significantly reduced rSap6 induced PAR2 levels and p38 phosphorylation, while pretreatment with either RGD peptide or anti-integrin Ab blocked Sap6 induced MKP1 phosphorylation without affecting p38 phosphorylation or PAR2 levels. (B) IL-1β (grey bars) and IL-8 (black bars) cytokine levels were measured by ELISA. OECs pretreated with RGD peptide or anti-integrin Ab prior to Sap6 stimulation resulted in an approximately six-fold reduction in IL-1β, similar to that induced by rSap6 ΔRGD , while addition of Sap6 (Inact) or pretreatment with PAR2-ANT resulted in equivalent production of rSap6. OECs pretreated with PAR2-ANT or with Sap6 (Inact) resulted in 10 fold reduction in IL-8 while pretreatment with RGD peptide or anti-integrin Ab prior to Sap6 stimulation did not alter IL-8 release. Data are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. P values are p ≤ 0.001 (***) and p ≤ 0.00001 (****).