FIGURE 2.
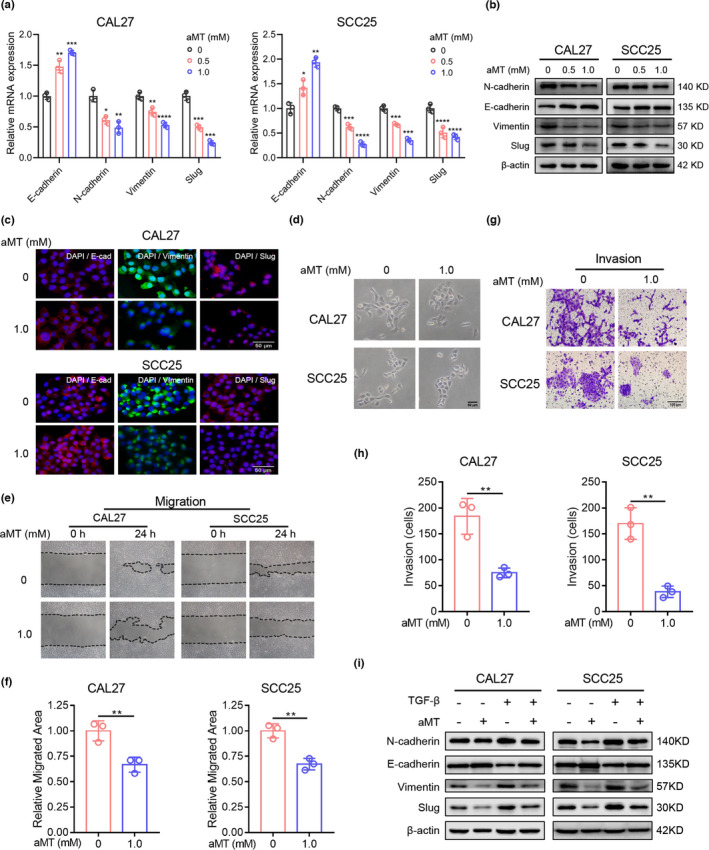
Melatonin inhibits the EMT of HNSCC cells. (A) RT‐qPCR analysis of EMT‐related markers. GAPDH was used as the internal reference gene. One‐way ANOVA. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. (B) Western blot analysis of EMT‐related markers, E‐cadherin, N‐cadherin, vimentin, and Slug in CAL27 and SCC25 cells treated with indicated concentrations of melatonin (aMT) for 24 h. β‐Actin was used as the loading control. (C) Cell immunofluorescence analysis of EMT‐related markers, E‐cadherin, vimentin, and Slug. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Representative photographs of the morphology of CAL27 and SCC25 cells treated with melatonin (1 mM) for 24 h. Scale bar, 50 μm. (E–H) Wound healing assay and Matrigel invasion assay were performed and analyzed to determine the migration and invasion abilities of CAL27 and SCC25 cells pretreated with melatonin (1 mM) for 24 h. Scale bar, 100 μm. Student's t test. (I) Western blot analysis of EMT‐related markers in CAL27 and SCC25 cells treated with TGF‐β (10 ng/ml) and melatonin (1 mM) for 48 h. Independent experiments were performed in triplicate. Values are represented as means ± SD
