FIGURE 8.
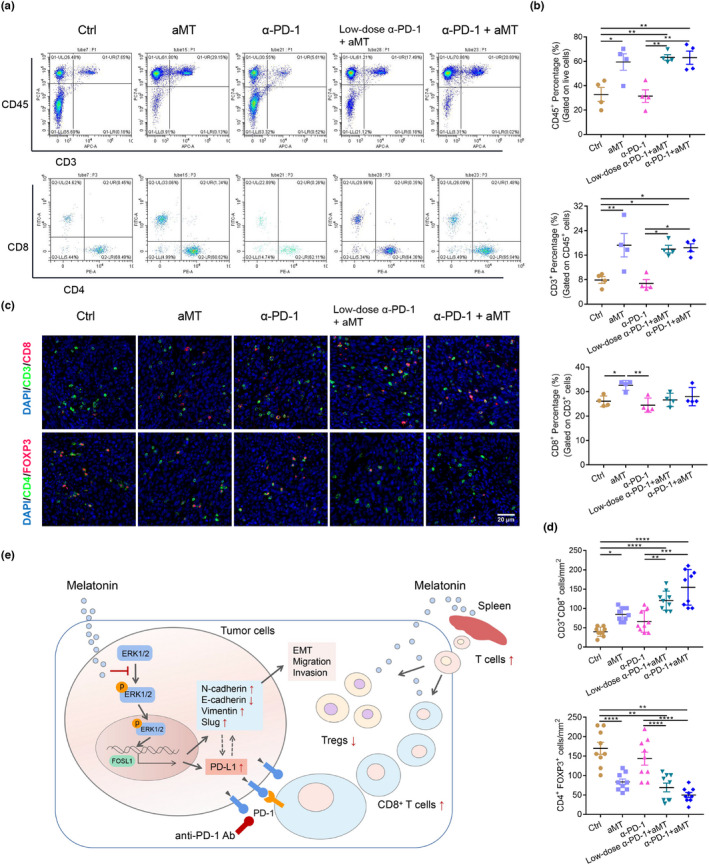
Combination therapy with melatonin and anti‐PD‐1 antibody enhances anti‐tumor immunity. (A) Flow cytometry was performed to determined the T cell population in spleens of tumor‐bearing C3H mice. (B) Percentages of CD45+, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in spleens were calculated and analyzed using one‐way ANOVA. (C) Representative immunofluorescence images of the tumors (day 23) stained with CD8 (red), CD3 (green), and DAPI (blue); CD4 (green), FOXP3 (red), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Numbers of CD3+CD8+ T cells and CD4+FOXP3+ cells per tumor area (mm2) in three randomly selected fields in each tumor section, n = 3 mice. One‐way ANOVA, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. (E) Schematic diagram illustrates the roles of melatonin in HNSCC. Melatonin inhibits EMT and downregulates PD‐L1 expression through the ERK1/2/FOSL1 pathway. Furthermore, melatonin exerts synergistic effects with anti‐PD‐1 antibody by increasing the CD8+ T cell proportion in spleens and the tumor microenvironment and by reducing Treg infiltration
