FIGURE 3.
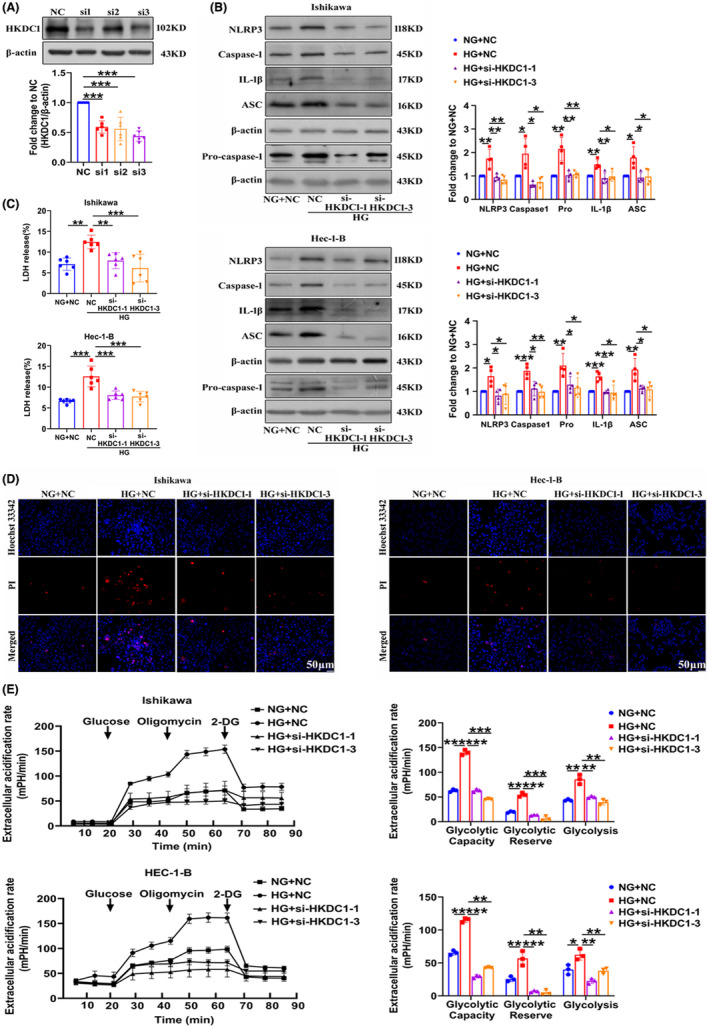
HKDC1 regulates pyroptosis and glycolysis in Ishikawa and Hec‐1‐B cells exposed to HG. (A) The interference efficiency of the HKDC1 siRNAs (n = 6). (B) The expression of pyroptosis‐related proteins in EC cells transfected with NC and HKDC1 siRNAs cultured under high and normal glucose conditions (n = 4). (C) The changes in LDH release from EC cells transfected with NC and HKDC1 siRNAs were measured (n = 6). (D) Representative cells staining with PI (red) and Hoechst 33342 (blue), (n = 3), scale bars = 50 µm. (E) Glycolysis, glycolytic reserve, and nonglycolytic acidification in EC cells were measured using a Seahorse XFe24 extracellular flux analyzer (n = 3). All values are presented as the means ± SD, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001. EC, endometrial cancer; HG, high glucose; NC, negative control; NG, normal glucose; si‐HKDC1, small interfering RNA targeting HKDC1
