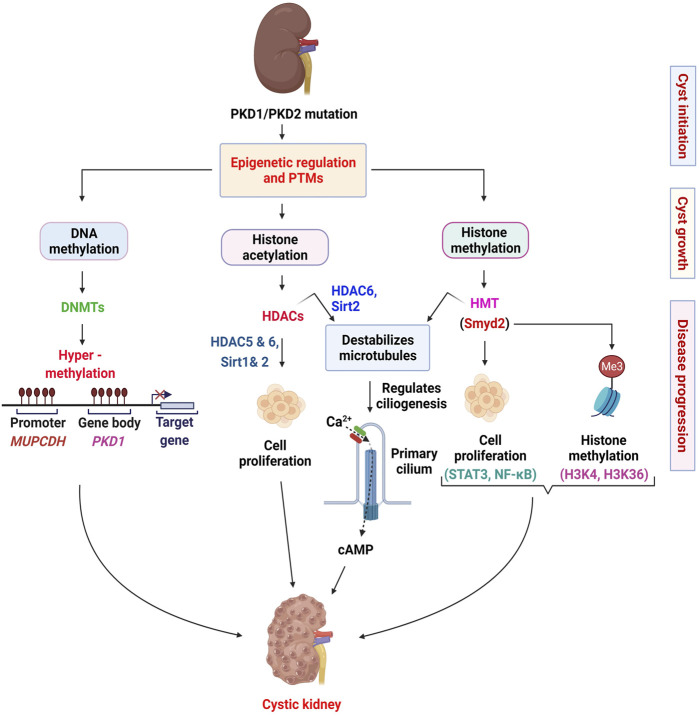
FIGURE 1.
Epigenetic mechanisms implicated in the pathogenesis of ADPKD. In this scheme, we summarize the roles of DNA methyl transferases (DNMTs), histone deacetylases (HDACs), and histone methyl transferases (HMTs) in renal epithelial cells. We indicate the roles of DNMTs in regulating the transcription of PKD1 and MUPCDH genes. In general, we indicate the HDACs and the HMT involved in regulating cell proliferation associated pathways. We also depict the role of HDACs and HMTs in regulating ciliogenesis through deacetylation of α-tubulin (HDAC6 and SIRT2) and methylation of α-tubulin (Smyd2). The involvement of calcium signaling in these processes is possible but uncertain. The various stages of ADPKD (cyst initiation, cyst growth and disease progression) require different epigenetic controls and therefore may require different therapeutic approaches.