Figure 1.
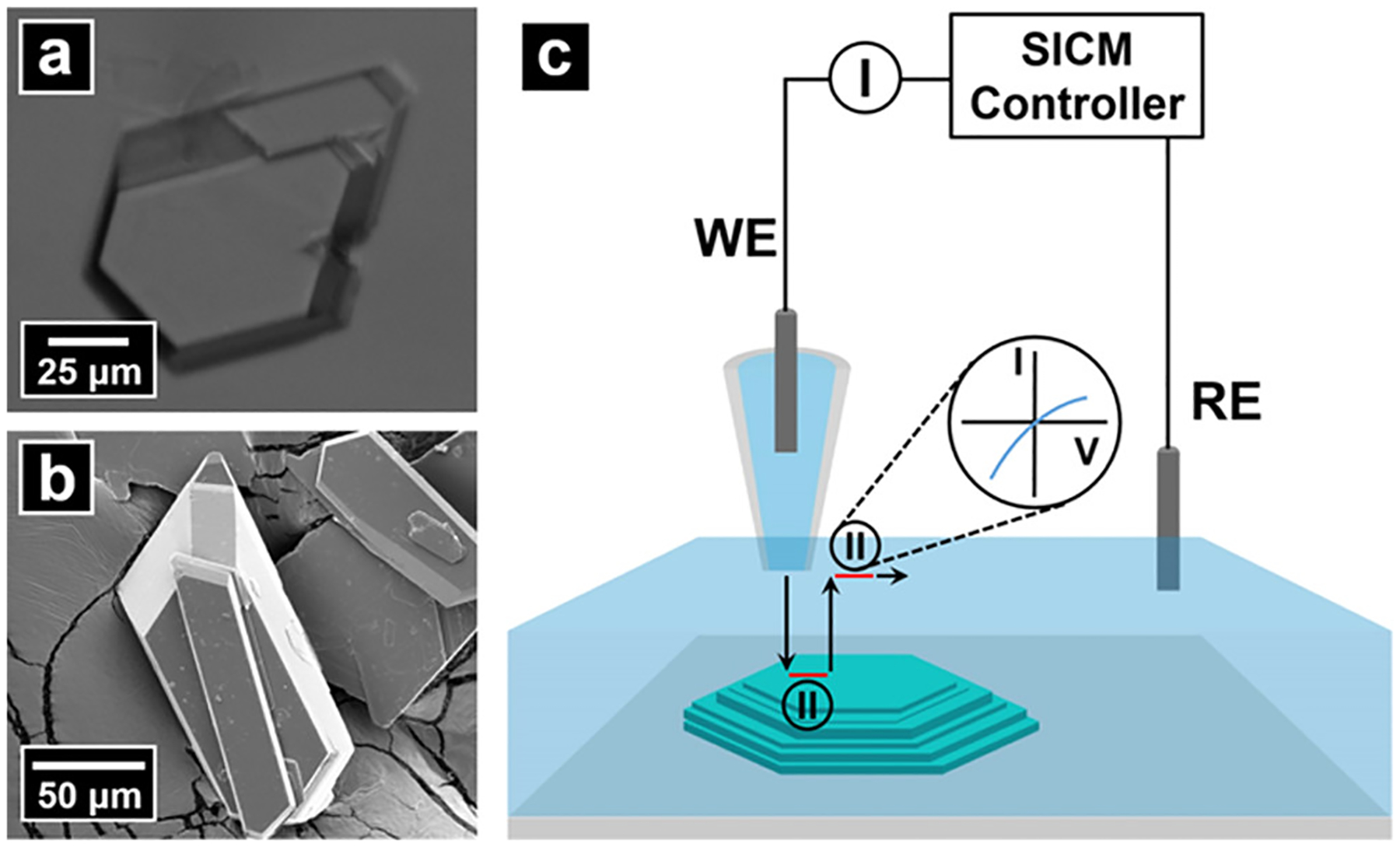
(a) Optical and (b) electron micrographs of dickite crystals examined. (c) Schematic for SICM measurements. An electrolyte-filled nanopipette was used as the probe and contained a back-inserted Ag/AgCl electrode (WE). A second Ag/AgCl electrode was placed in the bulk electrolyte and functioned as the RE. A potential difference was applied between the WE and RE to generate ion current for feedback control. Surface charge measurement was conducted by introducing an additional “pause state” when the pipette approached close to (extended) and retracted away from (retracted) the sample surface. At pause states, the feedback of SICM was disabled temporally, and the applied potential was swept to acquire a current–voltage response. Surface charge on the sample surface was then calculated at each pixel based on the difference of I–Vs at the extended position and retracted position.
