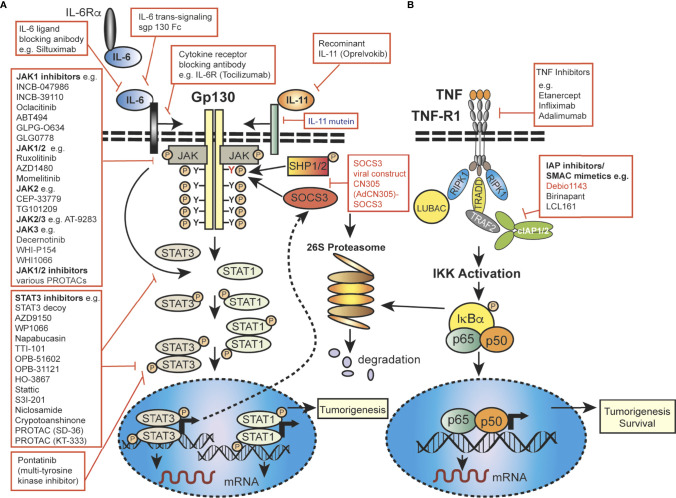
Figure 2.
Mechanistic diagram of JAK-STAT and TNFR signalling and modes of inhibition. (A) The gp130 receptor complex and signaling pathways for IL-6 and IL-11 are shown as key activators of STAT transcription factors. The intracellular domain of the gp130 receptor contains a membrane-proximal tyrosine (Y; red), which provides a docking site for the suppressor for SOCSs proteins (e.g. SOCS3) and SHP2, while the membrane-distal tyrosine (Y) sites permits interactions with the SH2 domain of STAT1/3. The membrane proximal Y sites are phosphorylated by JAKs and upon phosphorylation of the distal Y site, STAT1 and STAT3 are recruited, homo-dimerise and are translocated into the nucleus, where they bind to specific target genes to regulate their expression. (B) Simplified schematic diagram of TNF/TNFR1 signaling pathway with downstream interacting proteins indicated. (A, B) Red arrows indicate intervention/inhibition points within each pathway and red boxes list examples of JAK-STAT or cytokine inhibitors/modifying drugs with their target protein.