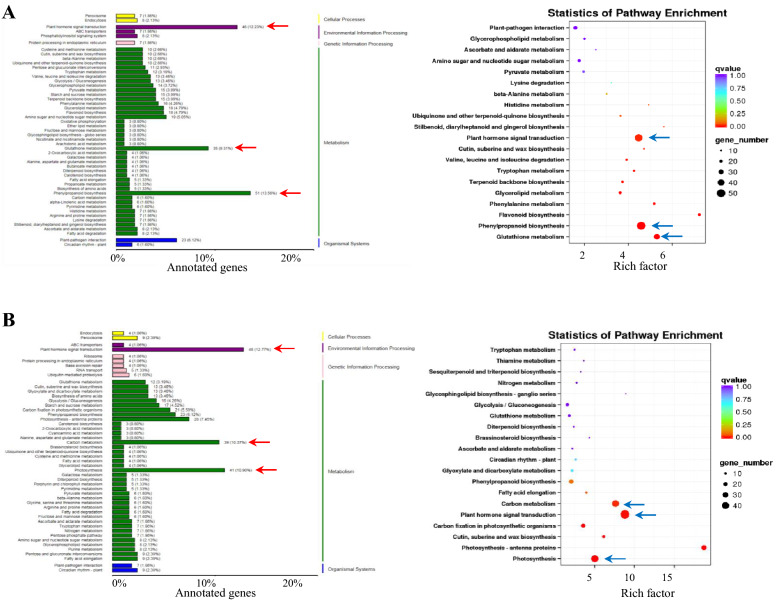
Fig. 4.
KEGG analysis of up-and down-regulated genes after TSA treatment. KEGG analysis was performed and the differentially expressed genes were classified into five categories: cell process, environmental information processing, genetic information processing, metabolism, and organismal systems. The top 50 pathways were presented here. A Among the up-regulated genes, metabolism accounted for the largest proportion of all the categories. Furthermore, the plant hormone signal transduction (46 genes), glutathione metabolism (35 genes), and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathways (51 genes) showed the most genes (red arrows). The statistical analysis of enrichment pathways showing the lowest q-value of plant hormone signal transduction, carbon metabolism, and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathways also indicated the reliable enrichment significance (blue arrows). B In the down-regulated genes, plant hormone signal transduction (48 genes), photosynthesis (41 genes), and carbon metabolism pathways (39 genes) showed the most genes (red arrows). The statistical analysis of the three enrichment pathways showed their lowest q-value and the reliable significance of enrichment pathways (blue arrows). Statistics of pathway enrichment of DEGs were analyzed using Rich Factor and q-value. Circle size indicates the gene numbers of the different pathways, which is the ratio of differentially expressed gene numbers to all gene numbers in this pathway term. A larger size means a greater number of genes. Q-value is the corrected p-value ranging from 0 to 1, and a lower q-value means greater intensiveness