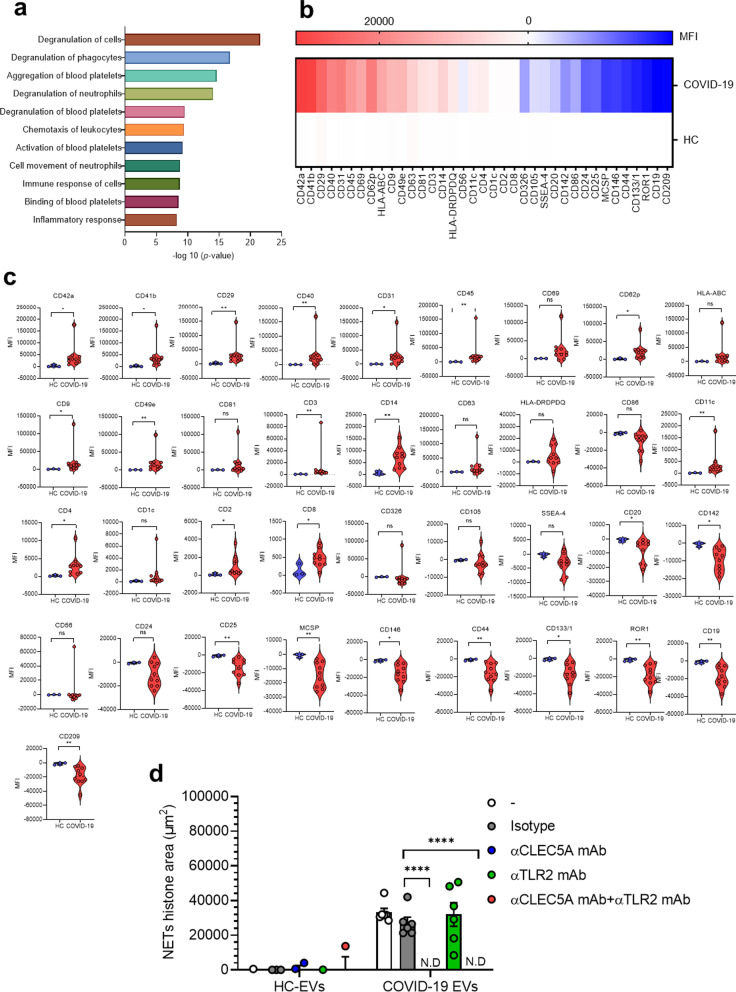
Fig. 2.
COVID-19 EVs are derived from activated platelets and induce NET formation via CLEC5A. a EVs from healthy controls (HCs-EVs, n = 2) and COVID-19 patients (COVID19-EVs, n = 5) were harvested by ultracentrifugation, then lysed in RIPA solution before subjected to mass spectrometry analysis. Proteins expressed in COVID-19 EVs, but not in HCs EVs, were further analyzed using the QIAGEN Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (QIAGEN IPA) software. Proteins which were expressed in all the COVID19-EVs were displayed. b, c HCs-EVs (n = 3) and COVID19-EVs (n = 10) were analyzed by flow cytometry, and markers highly activated in COVID-19 platelets were expressed as a heat map (b) or by mean fluorescence intensity (c). d Neutrophils were pre-incubated with anti-CLEC5A mAb (3E12A2, 10 μg/ml), anti-TLR2 mAb (# MAB2616, 10 μg/ml), or both anti-CLEC5A mAb (3E12A2, 10 μg/ml) and anti-TLR2 mAb (# MAB2616, 10 μg/ml), for 30 min at room temperature, followed by incubation with EVs (1 μg/ml) from COVID-19 patients (n = 6) at 37 °C for 3 h. Data are mean ± sd and repeats of at least three independent experiments. n.s.: no significant differences, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 (Student’s t-test). N.D: not detectable