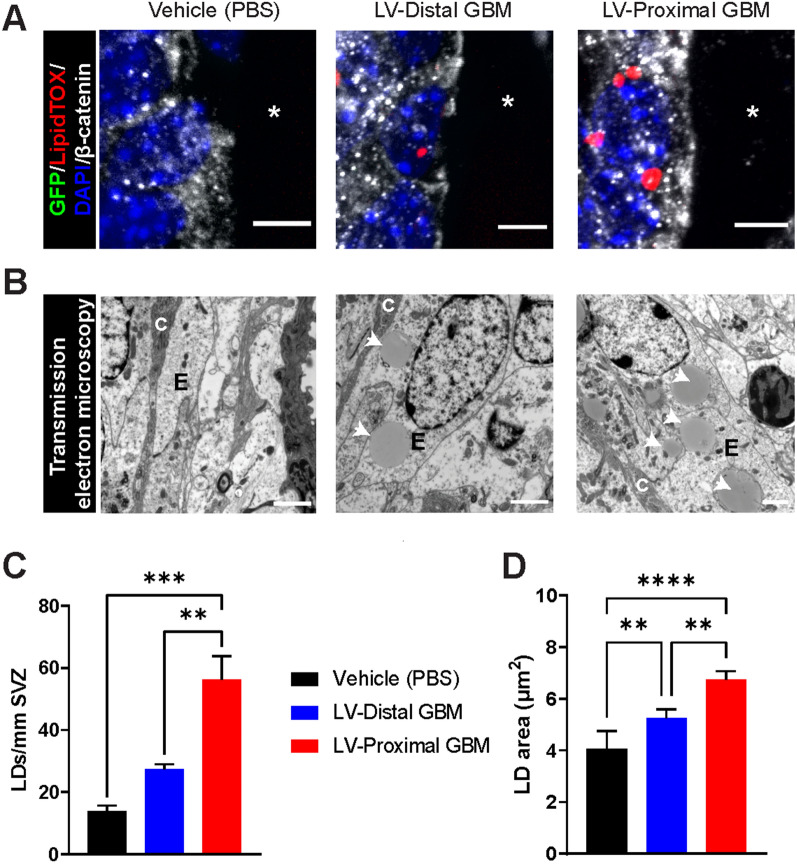
Fig. 3.
Lipid droplets accumulate in ependymal cells dependent on tumor proximity to the lateral ventricle. A Representative coronal immunohistochemistry images in vehicle (left), LV-distal GBM (middle), and LV-proximal GBM (right) showing the accumulation of lipid droplets within β-catenin + ependymal cells with increasing tumor proximity to the LV (n = 5). The lateral ventricle is indicated with a white asterisk. Scale bar = 5 µm. B Representative transmission electron microscopy images of the SVZ ependymal cells in vehicle (left), LV-distal GBM (middle), and LV-proximal GBM (right) showing lipid droplet accumulation with LV-proximal GBM (n = 3). Ependymal cells are indicated with “E”, and cilia are indicated with “C”. White arrows indicate lipid droplets. Scale bar = 2 µm. C Quantification of number of lipid droplets per mm of SVZ between vehicle, LV-distal GBM, and LV-proximal GBM groups measured using TEM analysis (n = 3 per group). D Quantification of lipid droplet area (µm2) between vehicle, LV-distal GBM, and LV-proximal GBM groups measured using TEM analysis (n = 3 per group). The data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. Statistical test used was ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc correction. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Non-significant interactions are not indicated