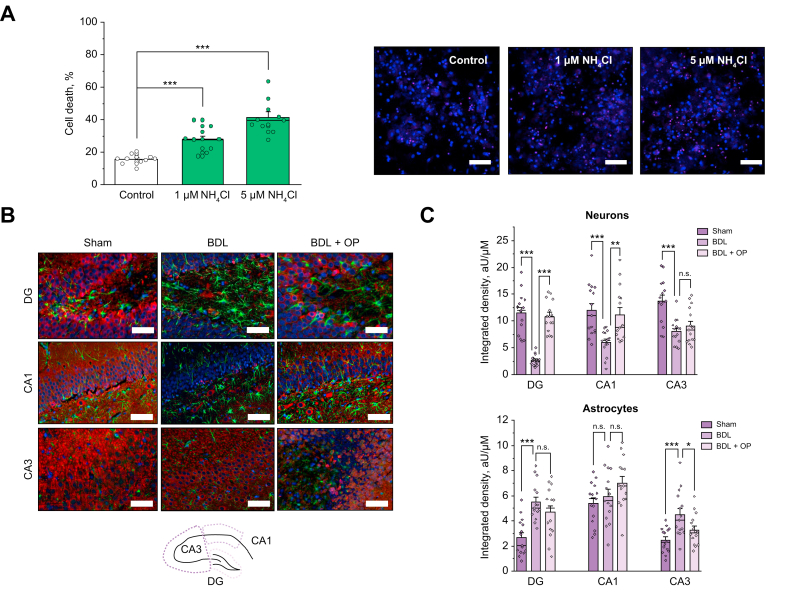
Fig. 6.
Cell death in in vitro and ex vivo models of hyperammonaemia.
(A) Cell death rate assessed in primary co-culture of neurons and astrocytes upon the application of low (1 μM) and higher (5 μM) concentrations of NH4Cl (red: propidium iodide, non-viable cells; blue: Hoechst, total number of cells). (B) Immunostaining of neurons and astrocytes of fixed brain slices from sham-operated animals and those subjected to BDL and to BDL/OP from the DG, CA1, and CA3 areas from the rat hippocampus (green: GFAP, astrocytic marker; red: beta III tubulin, neuronal marker; blue: DAPI, cell nuclei). Scale bar = 250 μm. (C) Inset: schematic overview of the areas in rat hippocampus. Quantification bar charts for cell density in the DG, CA1, and CA3 areas for both neurons (upper chart) and astrocytes (lower chart). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.001, ∗∗∗p <0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. BDL, bile duct ligation; CA1, cornu ammonis 1; CA3, cornu ammonis 3; DG, dentate gyrus; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; OP, ornithine phenylacetate.