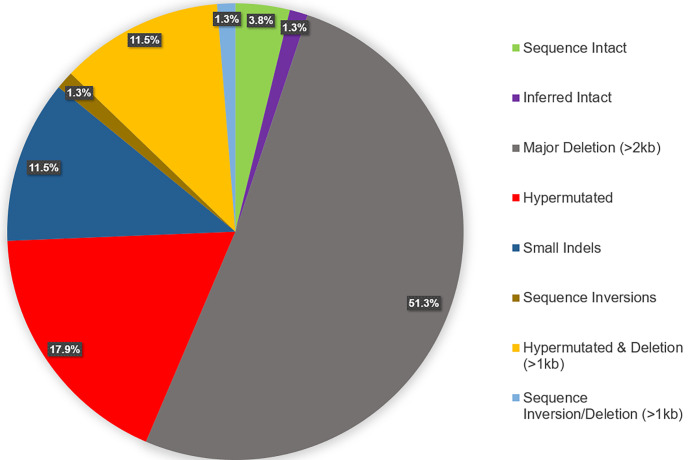
FIG 5.
Summary of HIV-1 proviral structures sequenced from five subtype B-positive individuals. All proviruses were evaluated manually initially for the determination of sequence length and defectiveness, and sequences of full-length proviruses were evaluated for intactness by the ProSeq-IT tool (29). Of the 88 proviruses sequenced (and after removing duplicate clonal sequences from the analysis), 3.8% (n = 3) were sequence intact and confirmed to be replication competent by a qVOA by Halvas et al. (15), 1.3% (n = 1) were inferred intact by ProSeq-IT (29), 51.3% (n = 40) contained major genomic deletions of >2 kb in length, 17.9% (n = 14) were hypermutated according to the Los Alamos Hypermut v2 program (P value of <0.05), 11.5% (n = 9) both were hypermutated and contained genomic deletions of >1 kb in length, 1.3% (n = 1) contained sequence inversions and contained genomic deletions of >1 kb in length, 11.5% (n = 9) were defective due to small indels, and 1.3% (n = 1) contained genomic inversions.