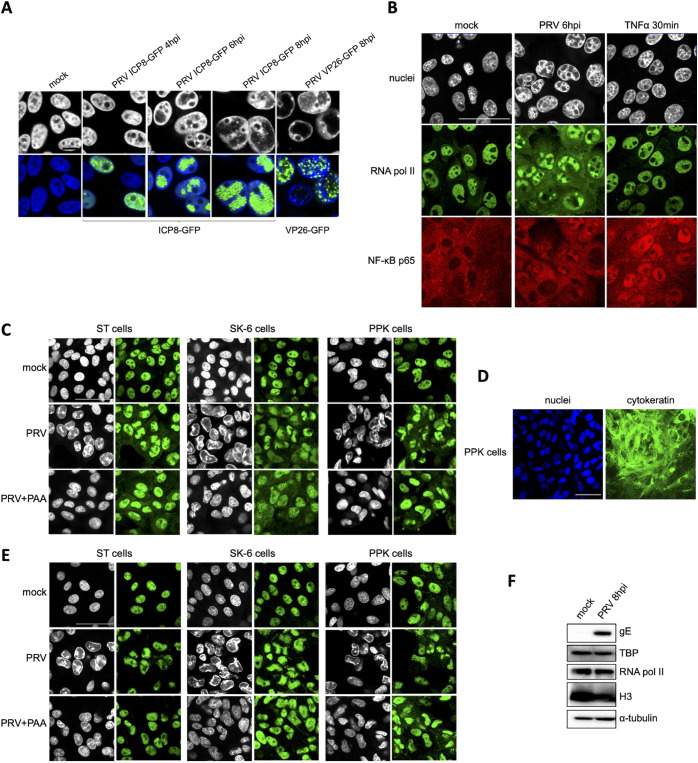
FIG 2.
PRV infection results in substantial sequestration of NF-κB p65, RNA polymerase II, and TATA box binding protein (TBP) in nuclear virus replication compartments (VRCs). (A) Confocal microscopy pictures of ST cells infected with PRV ICP8-GFP (PRV 926, MOI of 10) at 4, 6, and 8 hpi or with PRV VP26-GFP (PRV GS443, MOI of 10) at 8 hpi. Viral proteins fused to GFP are shown in green, and the counterstained cell nuclei are represented in gray (upper row) or blue (lower row). Bar, 10 μm. (B) Confocal microscopy pictures of RNA polymerase II (in green) and NF-κB p65 (in red) in ST cells infected with PRV at 6 hpi (PRV WT Kaplan, MOI of 10) or treated with 100 ng/mL porcine TNF-α for 30 min. Cell nuclei are shown in gray. Bar, 50 μm. (C) Confocal microscopy pictures of RNA polymerase II (in green) in PRV-infected ST, SK-6, and PPK cells (PRV WT Kaplan, MOI of 10). ST and PPK cells were fixed at 6 hpi, while SK-6 cells were fixed at 8 hpi. The counterstained cell nuclei are shown in gray. Bar, 50 μm. (D) Confocal microscopy pictures of PKK cells stained for pancytokeratin (in green). Cell nuclei are shown in blue. Bar, 50 μm. (E) Confocal microscopy pictures of TBP (in green) in PRV-infected PPK, ST, and SK-6 cells at 6 hpi (ST and PPK) and 8 hpi (SK-6) (PRV WT Kaplan, MOI of 10). The counterstained cell nuclei are shown in gray. Bar, 50 μm. (F) Western blot analysis of RNA polymerase II and TBP in mock-infected and PRV-infected ST cells at 8 hpi (PRV WT Kaplan, MOI of 10). Detection of the viral gE protein served as the infection control, whereas H3 and α-tubulin protein levels were used as loading controls for nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins, respectively.