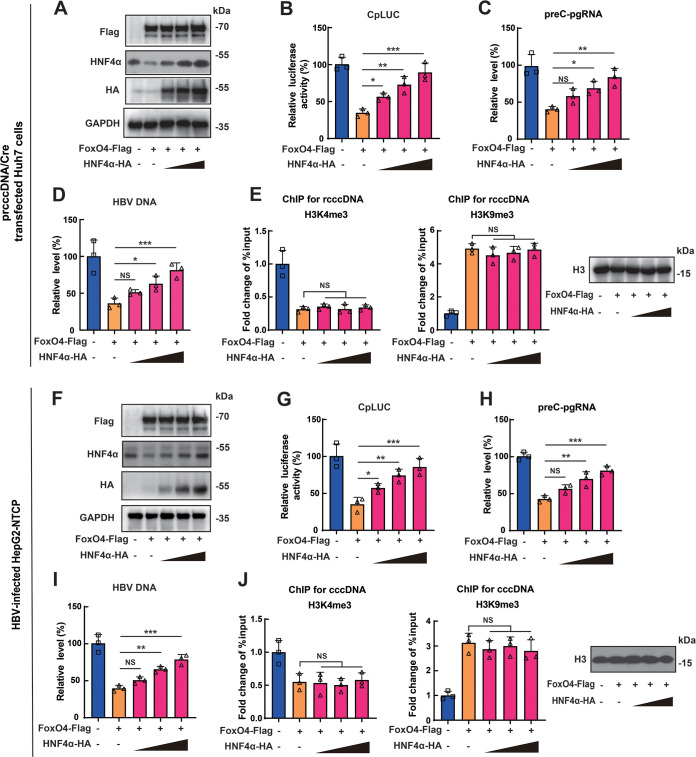
FIG 4.
FoxO4-mediated epigenetic suppression of HBV cccDNA is not due to its effect on HNF4α expression. (A and B) The HBV core promoter-dependent reporter plasmid (CpLUC) was transfected into Huh7 cells together with FoxO4-Flag in the absence or presence of increasing doses of HNF4α-HA. At 48 h posttransfection, the protein levels of FoxO4 and HNF4α were determined by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies (A), and the HBV core promoter activity was determined by luciferase assay (B). (C and D) prcccDNA/Cre was transfected into Huh7 cells together with FoxO4-Flag in the absence or presence of increasing doses of HNF4α-HA. At 48 h posttransfection, the levels of preC-pgRNA (C) and HBV DNA (D) were detected by qRT-PCR and qPCR, respectively. (E) Cells were treated as in panels C and D, and the effect of FoxO4 on the recruitment of H3K4me3 and H3K9me3 onto rcccDNA was determined by ChIP assays. The data are shown as the fold change to empty vector-transfected cells after normalized to input and control IgG. (F and G) CpLUC and FoxO4-Flag were cotransfected into HepG2-NTCP cells in the absence or presence of increasing doses of HNF4α-HA. At 48 h posttransfection, the protein levels of FoxO4 and HNF4α were determined by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies (F), and the HBV core promoter activity was determined by a luciferase assay (G). (H to J) FoxO4-Flag was transfected into HepG2-NTCP cells in the absence or presence of increasing doses of HNF4α-HA. at 48 h posttransfection, the cells were then infected with HBV at 103 vge/cell. At day 9 postinfection, levels of preC-pgRNA (H) and HBV DNA (I) were detected by qRT-PCR and qPCR, respectively, and at day 3 postinfection, the effect of FoxO4 on the recruitment of H3K4me3, H3K9me3 to cccDNA was determined by ChIP assay (J). The data are shown as means ± the SD of triplicates and are representative of three independent experiments (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; NS, no significance).